This article explains Amazon review scraping methods. This process effectively exports Amazon reviews to Excel or other formats for easier access and use.
There are three methods to scrape Amazon reviews:
- Amazon review scraping with coding: Building a web scraper in Python or JavaScript
- Amazon review scraping without coding:
- Using the ScrapeHero Cloud’s Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings Scraper, a no-code scraping tool
- Using the ScrapeHero Cloud’s Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings API
ScrapeHero Cloud offers you ready-made web crawlers and real-time APIs, which are the easiest way to extract data from websites and download it into spreadsheets with a few clicks.
Don’t want to code? ScrapeHero Cloud is exactly what you need.
With ScrapeHero Cloud, you can download data in just two clicks!
Build an Amazon Review Scraper in Python/JavaScript
In this section, we will guide you on how to scrape Amazon reviews using either Python or JavaScript. We will utilize the browser automation framework called Playwright to emulate browser behavior in our code.
One of the key advantages of this approach is its ability to bypass common blocks often put in place to prevent scraping. However, familiarity with the Playwright API is necessary to use it effectively.
You could also use Python Requests, BeautifulSoup, or LXML to build an Amazon reviews scraper without using a browser or a browser automation library for web scraping Amazon reviews. However, bypassing the anti-scraping mechanisms put in place can be challenging and is beyond the scope of this article.
Here are the steps to scrape Amazon reviews using Playwright:
Step 1: Choose either Python or JavaScript as your programming language.
Step 2: Install Playwright for your preferred language:
Python
pip install playwright
# to download the necessary browsers
playwright installJavaScript
npm install playwright@latestStep 3: Write your code to emulate browser behavior and extract Amazon product reviews scraping details using the Playwright API. You can use the code provided below:
Python
import asyncio
import json
from playwright.async_api import async_playwright
url = " https://www.amazon.com/Crocs-Unisex-Classic-Black-Women/dp/B0014C2NBC/ref=sr_1_3?crid=2WI0QM6BYFKLZ&keywords=crocs&qid=1696915791&s=amazon-devices&sprefix=croc%2Camazon-devices%2C449&sr=1-3"
max_pagination = 2
async def extract_data(page) -> list:
"""
Parsing details from the listing page
Args:
page: webpage of the browser
Returns:
list: details of homes for sale
"""
# Initializing selectors and xpaths
seemore_selector = "//div[@id='reviews-medley-footer']//a"
div_selector = "[class='a-section celwidget']"
next_page_selector = "[class='a-last']"
name_xpath = "//a[@class='a-profile']//span[@class='a-profile-name']"
rate_xpath = "//a//i[contains(@class,'review-rating')]/span"
review_title_xpath = "//a[contains(@class, 'review-title')]/span[2]"
review_date_xpath = "//span[contains(@class,'review-date')]"
review_text_xpath = "[data-hook='review-body']"
# navigating to reviewpage
review_page_locator = page.locator(seemore_selector)
await review_page_locator.hover()
await review_page_locator.click()
# List to save the details of properties
amazon_reviews_ratings = []
# Paginating through each page
for _ in range(max_pagination):
# Waiting for the page to finish loading
await page.wait_for_load_state("load")
# Extracting the elements
review_cards = page.locator(div_selector)
cards_count = await review_cards.count()
for index in range(cards_count):
# Hovering the element to load the price
inner_element = review_cards.nth(index=index)
await inner_element.hover()
inner_element = review_cards.nth(index=index)
# Extracting necessary data
name = await inner_element.locator(name_xpath).inner_text() if await inner_element.locator(name_xpath).count() else None
rate = await inner_element.locator(rate_xpath).inner_text() if await inner_element.locator(rate_xpath).count() else None
review_title = await inner_element.locator(review_title_xpath).inner_text() if await inner_element.locator(review_title_xpath).count() else None
review_date = await inner_element.locator(review_date_xpath).inner_text() if await inner_element.locator(review_date_xpath).count() else None
review_text = await inner_element.locator(review_text_xpath).inner_text() if await inner_element.locator(review_text_xpath).count() else None
# Removing extra spaces and unicode characters
name = clean_data(name)
rate = clean_data(rate)
review_title = clean_data(review_title)
review_date = clean_data(review_date)
review_text = clean_data(review_text)
data_to_save = {
"reviewer_name": name,
"rate": rate,
"review_title": review_title,
"review_date": review_date,
"review_text": review_text
}
amazon_reviews_ratings.append(data_to_save)
next_page_locator = page.locator(next_page_selector)
# Check if the "Next Page" button exists
if await next_page_locator.count() > 0:
await next_page_locator.hover()
await next_page_locator.click()
else:
break
save_data(amazon_reviews_ratings, "Data.json")
async def run(playwright) -> None:
# Initializing the browser and creating a new page.
browser = await playwright.firefox.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
page = await context.new_page()
await page.set_viewport_size({"width": 1920, "height": 1080})
page.set_default_timeout(120000)
# Navigating to the homepage
await page.goto(url, wait_until="domcontentloaded")
await extract_data(page)
await context.close()
await browser.close()
def clean_data(data: str) -> str:
"""
Cleaning data by removing extra white spaces and Unicode characters
Args:
data (str): data to be cleaned
Returns:
str: cleaned string
"""
if not data:
return ""
cleaned_data = " ".join(data.split()).strip()
cleaned_data = cleaned_data.encode("ascii", "ignore").decode("ascii")
return cleaned_data
def save_data(product_page_data: list, filename: str):
"""Converting a list of dictionaries to JSON format
Args:
product_page_data (list): details of each product
filename (str): name of the JSON file
"""
with open(filename, "w") as outfile:
json.dump(product_page_data, outfile, indent=4)
async def main() -> None:
async with async_playwright() as playwright:
await run(playwright)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())JavaScript
const { chromium, firefox } = require('playwright');
const fs = require('fs');
const url = "https://www.amazon.com/Crocs-Unisex-Classic-Black-Women/dp/B0014C2NBC/ref=sr_1_3?crid=2WI0QM6BYFKLZ&keywords=crocs&qid=1696915791&s=amazon-devices&sprefix=croc%2Camazon-devices%2C449&sr=1-3";
const maxPagination = 2;
/**
* Save data as list of dictionaries
as json file
* @param {object} data
*/
function saveData(data) {
let dataStr = JSON.stringify(data, null, 2)
fs.writeFile("data.json", dataStr, 'utf8', function (err) {
if (err) {
console.log("An error occurred while writing JSON Object to File.");
return console.log(err);
}
console.log("JSON file has been saved.");
});
}
function cleanData(data) {
if (!data) {
return;
}
// removing extra spaces and unicode characters
let cleanedData = data.split(/\s+/).join(" ").trim();
cleanedData = cleanedData.replace(/[^\x00-\x7F]/g, "");
return cleanedData;
}
/**
* The data extraction function used to extract
necessary data from the element.
* @param {HtmlElement} innerElement
* @returns
*/
async function extractData(innerElement) {
async function extractData(data) {
let count = await data.count();
if (count) {
return await data.innerText()
}
return null
};
// intializing xpath and selectors
const nameXpath = "//a[@class='a-profile']//span[@class='a-profile-name']";
const rateXpath = "//a//i[contains(@class,'review-rating')]/span";
const reviewTitleXpath = "//a[contains(@class, 'review-title')]/span[2]";
const reviewDateXpath = "//span[contains(@class,'review-date')]";
const reviewTextXpath = "[data-hook='review-body']";
let name = innerElement.locator(nameXpath);
name = await extractData(name);
let rate = innerElement.locator(rateXpath);
rate = await extractData(rate);
let reviewTitle = innerElement.locator(reviewTitleXpath);
reviewTitle = await extractData(reviewTitle);
let reviewDate = innerElement.locator(reviewDateXpath);
reviewDate = await extractData(reviewDate);
let reviewText = innerElement.locator(reviewTextXpath);
reviewText = await extractData(reviewText);
// cleaning data
name = cleanData(name)
rate = cleanData(rate)
reviewTitle = cleanData(reviewTitle)
reviewDate = cleanData(reviewDate)
reviewText = cleanData(reviewText)
extractedData = {
"reviewer's name": name,
'rate': rate,
'reviewTitle': reviewTitle,
'reviewDate': reviewDate,
'reviewText': reviewText
}
return extractedData
}
/**
* The main function initiate a browser object and handles the navigation.
*/
async function run() {
// initializing browser and creating new page
const browser = await firefox.launch({ headless: false });
const context = await browser.newContext();
const page = await context.newPage();
await page.setViewportSize({ width: 1920, height: 1080 });
page.setDefaultTimeout(120000);
// initializing xpath and selectors
const seeMoreSelector = "//div[@id='reviews-medley-footer']//a"
const divSelector = "[class='a-section celwidget']"
const nextPageSelector = "[class='a-last']"
// Navigating to the home page
await page.goto(url, { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded' });
// Navigating to Review page
const ReviewPageLocator = await page.$(seeMoreSelector);
await ReviewPageLocator.hover();
await ReviewPageLocator.click();
// Wait until the list of properties is loaded
await page.waitForSelector(divSelector);
// to store the extracted data
let data = [];
// navigating through pagination
for (let pageNum = 0; pageNum < maxPagination; pageNum++) {
await page.waitForLoadState("load");
await page.waitForTimeout(10);
let reviewCards = page.locator(divSelector);
reviewCardsCount = await reviewCards.count()
// going through each listing element
for (let index = 0; index < reviewCardsCount; index++) {
await page.waitForTimeout(2000);
await page.waitForLoadState("load");
let innerElement = await reviewCards.nth(index);
await innerElement.hover();
innerElement = await reviewCards.nth(index);
let dataToSave = await extractData(innerElement);
data.push(dataToSave);
};
//to load next page
const nextPageLocator = await page.$(nextPageSelector);
// Check if the "Next Page" button exists
if (nextPageLocator !== null) {
await nextPageLocator.hover();
await nextPageLocator.click();
} else {
// Exit the loop or perform other actions when the button is not found
break;
}
};
saveData(data);
await context.close();
await browser.close();
};
run();This code shows how to scrape Amazon reviews using the Playwright library in Python and JavaScript.
The corresponding scripts have two main functions, namely:
- run function: This function takes a Playwright instance as an input and performs the scraping process. The function launches a Chromium browser instance, navigates to Amazon, fills in a search query, clicks the search button, and waits for the results to be displayed on the page.
The save_data function is then called to extract the review details and store the data in a Data.json file. - save_data function: This function takes a Playwright page object as input and returns a list of dictionaries containing review details. The details include the reviewer’s name, the rating they gave , the review’s title, date of posting the review and the review text.
Finally, the main function uses the async_playwright context manager to execute the run function. A JSON file containing the listings of the Amazon reviews scraper script you just executed would be created.
Step 4: Run your code and collect the scraped reviews and ratings from Amazon.
Using No-Code Amazon Reviews Scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud
The Amazon Reviews and Ratings Scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud is a convenient method for scraping reviews and ratings from Amazon. It provides an easy, no-code method for scraping data, making it accessible for individuals with limited technical skills.
This section will guide you through the steps to set up and use the Amazon Reviews Scraper.
1. Sign up or log in to your ScrapeHero Cloud account.
2. Go to the Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings Scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud.
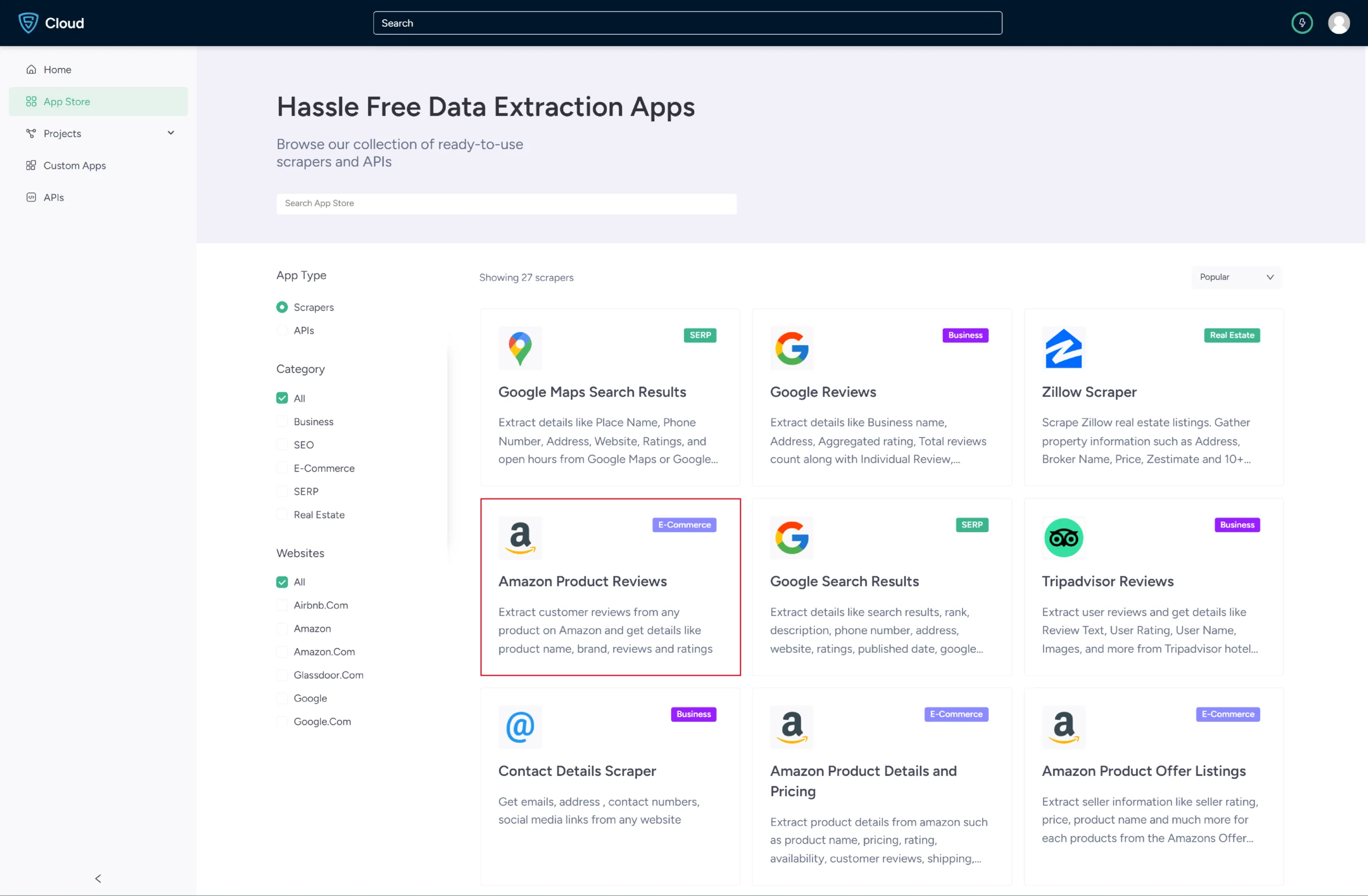
3. Click the Create New Project button.
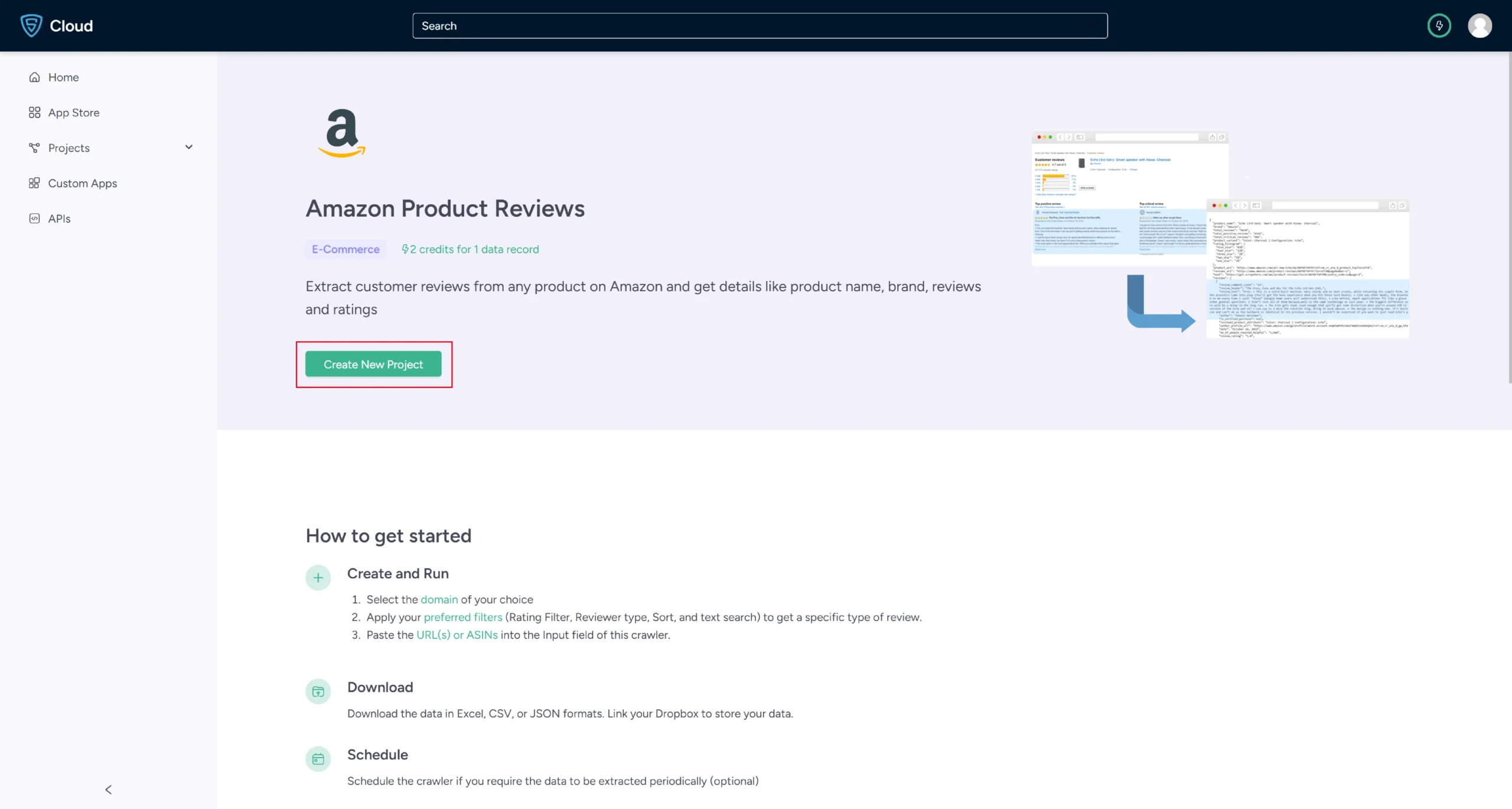
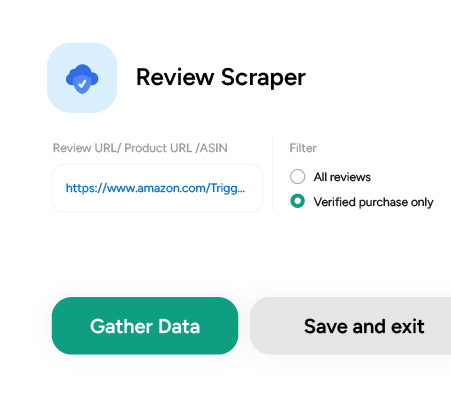
4. To scrape the details, you need to either provide product URL or ASIN.
- You can get the product URL from the Amazon search results page.
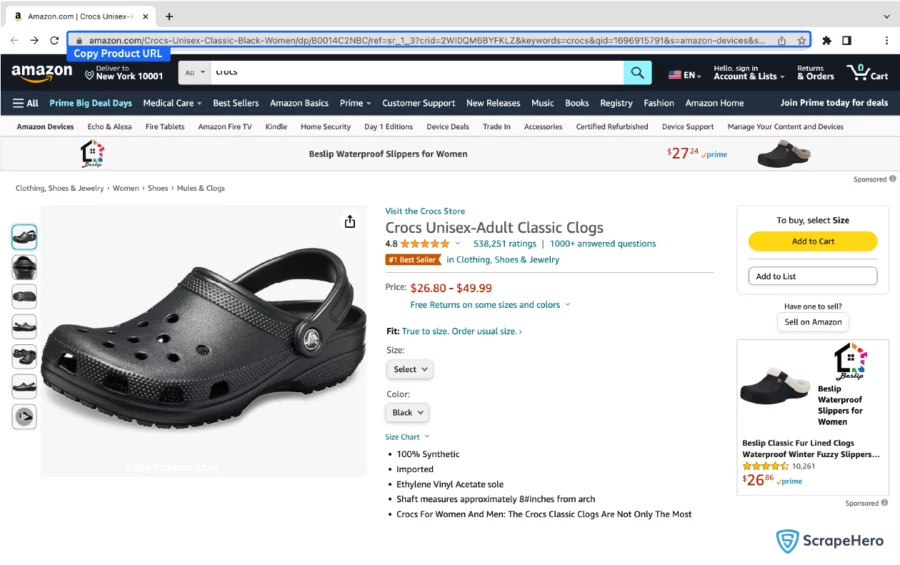
- You can get the product’s ASIN from the product information section of a product listing page.
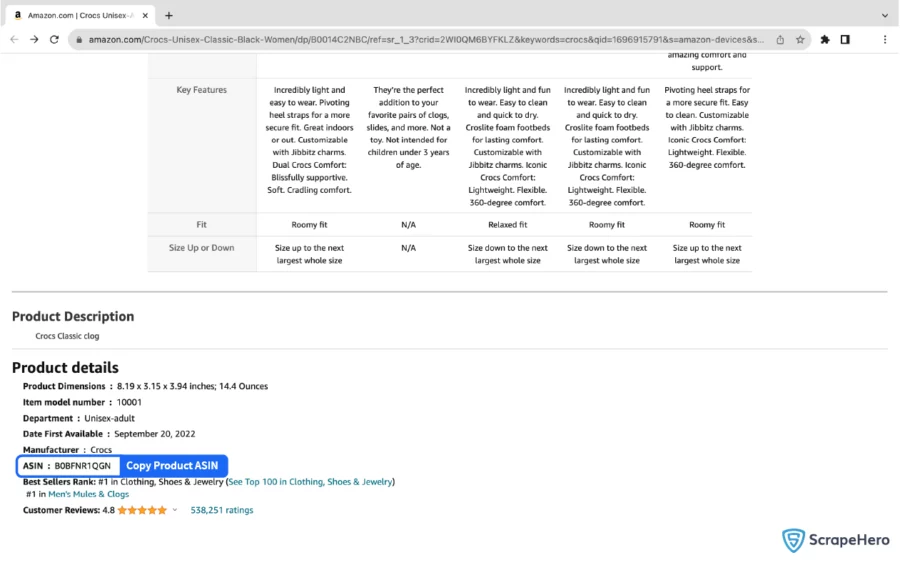
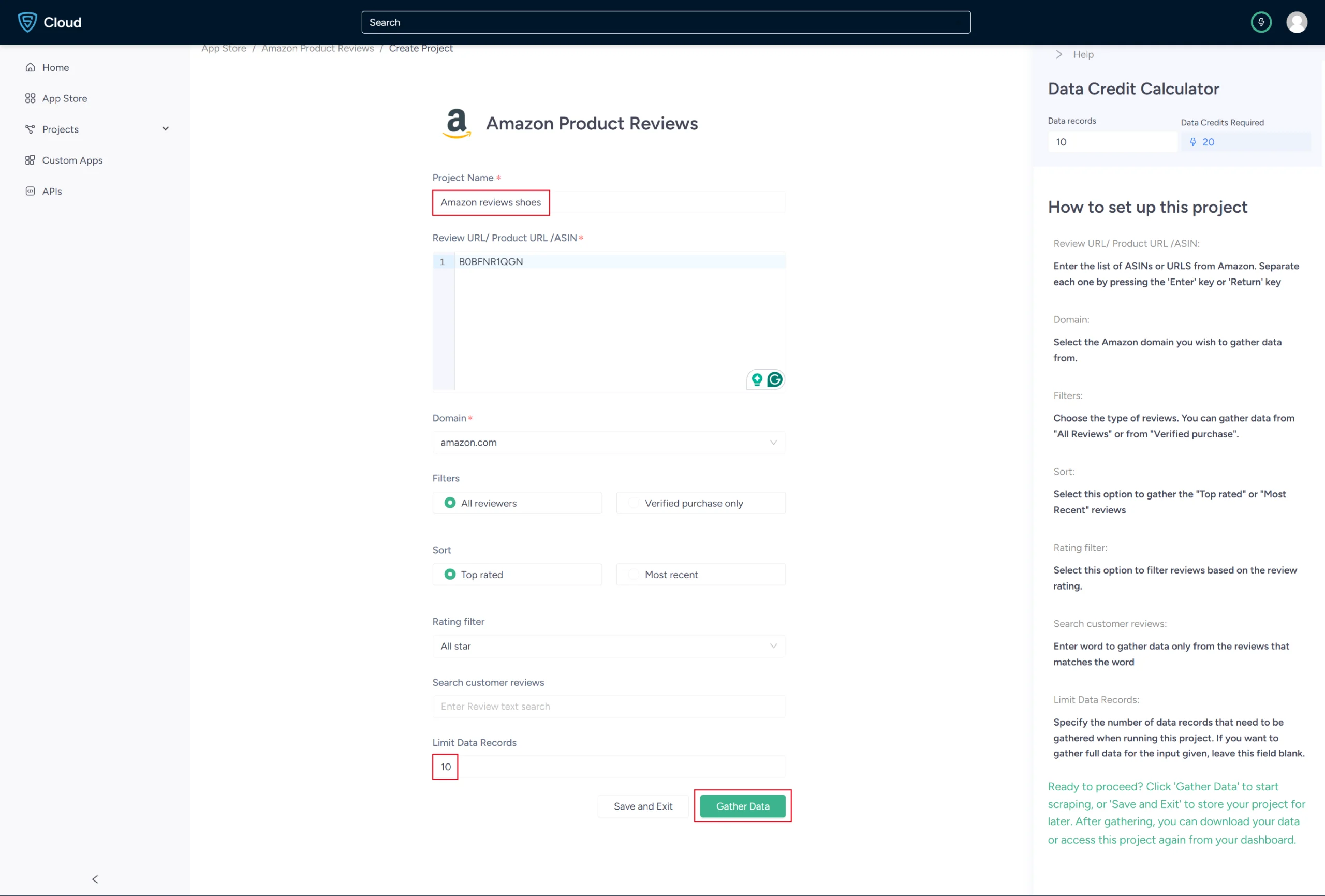
5. In the field provided, enter a project name, product URL, or ASIN, and the maximum number of records you want to gather.
You can also choose the type of reviews and filter reviews based on the review rating. Then, click the Gather Data button to start the scraper.
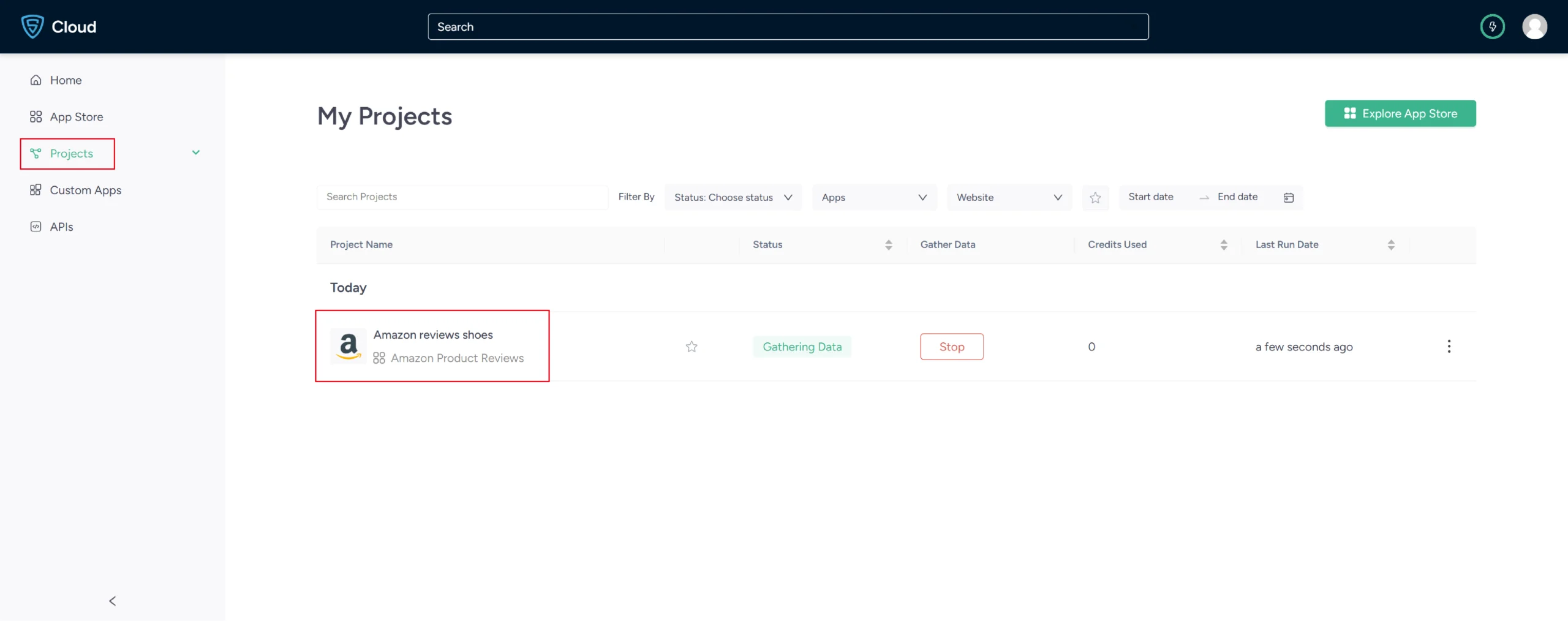
6. The scraper will start fetching data for your queries, and you can track its progress under the Projects tab.
7. Once it is finished, you can view the data by clicking on the project name. A new page will appear, and under the Overview tab, you can see and download the data.
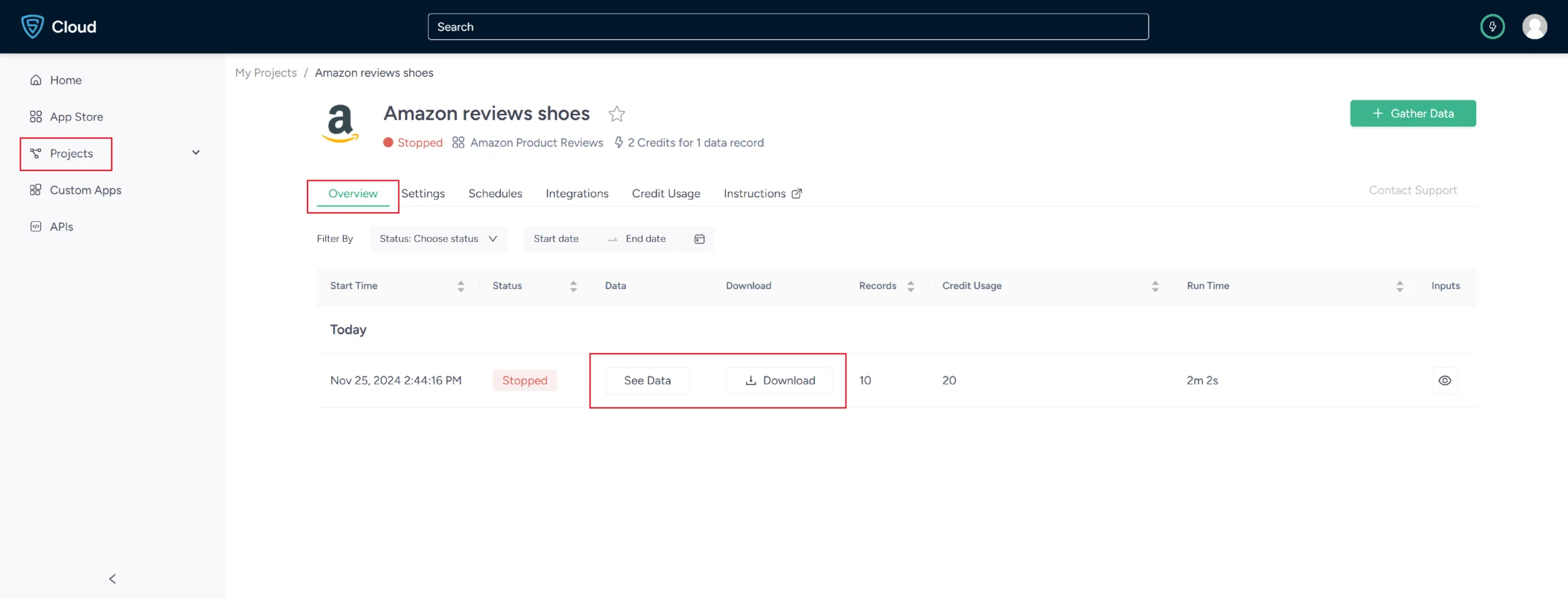
8. You can also pull Amazon review data into a spreadsheet from here. Just click on Download Data, select Excel, and open the downloaded file using Microsoft Excel.
Using Amazon Reviews API by ScrapeHero Cloud
The ScrapeHero Cloud Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings API is an alternate tool for extracting product details from Amazon. This user-friendly API enables those with minimal technical expertise to obtain product data effortlessly from Amazon.
This section will walk you through the steps to configure and utilize the Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings API provided by ScrapeHero Cloud.
Here are steps to configure and utilize this API:
1. Sign up or log in to your ScrapeHero Cloud account.
2. Go to the Amazon Product Reviews and Ratings API by ScrapeHero Cloud.
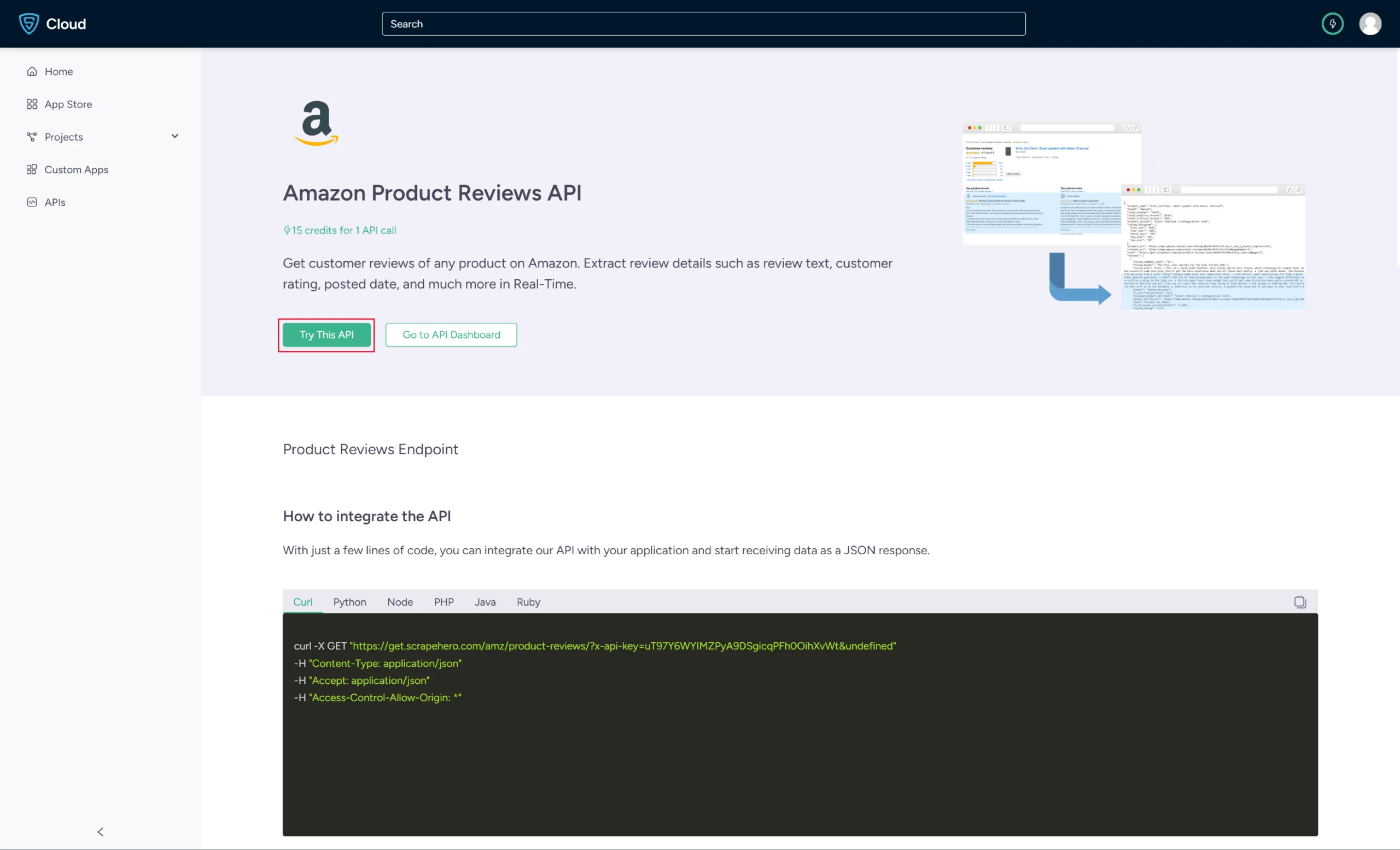
3. Click on the Try This API button.
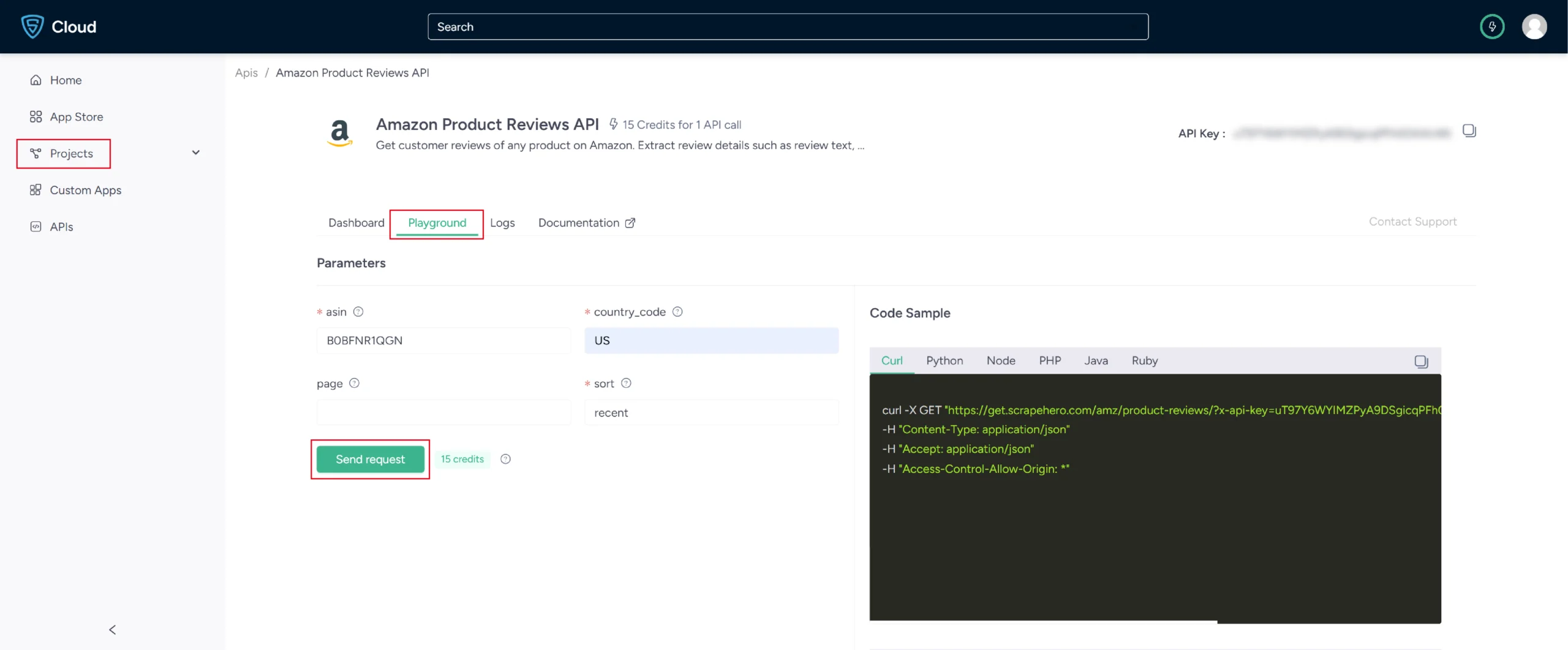
4. In the field provided enter the product ASIN. You can also provide the country code if you want. Click Send request.
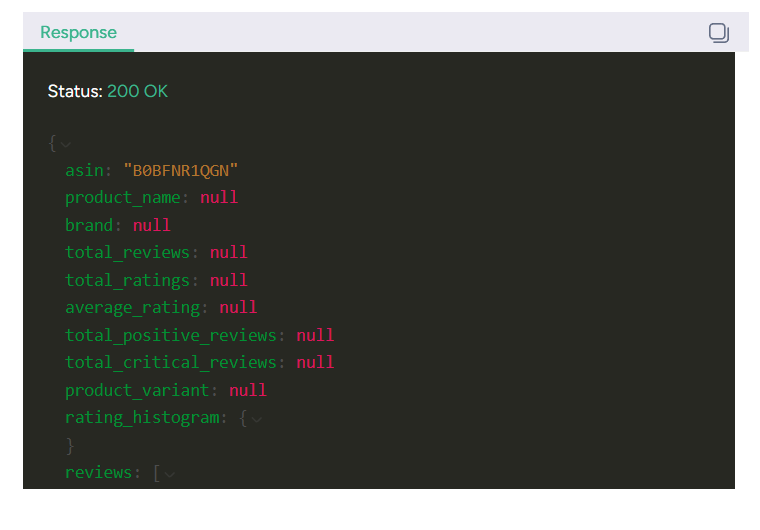
5. You will get the results in the response window on the bottom right side of the page.
Use Cases of Amazon Review Data
Why might you want to scrape product reviews and ratings from Amazon? Here are some use cases where this information can make a difference:
- Business Reputation Management
Managing your business reputation involves continuously monitoring how you’re perceived and dissecting customer opinions about your products and services. With detailed review data, you can gain deep insights into your operational strengths and areas needing improvement.
- Competitor Analysis
By examining competitor reviews, you can pinpoint their strengths and weaknesses, compare product features, and identify market gaps that your business can fill.
By monitoring reviews over time, you can detect shifts in consumer preferences and emerging challenges, enabling you to adapt your strategies proactively.
- Supply Chain Optimization
If multiple reviews point out issues with product delivery times or conditions upon arrival, this could signal a problem in your supply chain.
Data from reviews can help you identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies that need to be addressed, allowing you to make targeted improvements in your logistics and distribution.
- Customer Support Assessment
Reviews often mention customer service experiences, whether good or bad. By systematically analyzing this feedback, you can gauge the effectiveness of your customer support team.
This enables you to make necessary adjustments, whether it’s retraining staff or revising support protocols, to elevate customer satisfaction.
- Price Point Evaluation
Consumers often discuss whether a product offers good value for its price in their reviews. By monitoring these comments, you can assess whether your pricing strategy aligns with consumers’ perceptions of value.
For a deeper dive into analyzing customer feedback, check out our article on how to analyze Google reviews, which offers valuable insights into consumer sentiment and pricing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Amazon review scraping can be done with Python, JavaScript, or tools like ScrapeHero’s scrapers and APIs.
Yes, to prevent web scraping Amazon reviews, Amazon implements anti-scraping measures such as CAPTCHAs, IP blocking, and user-agent validation.
To scrape Amazon reviews using Python, you need to send HTTP requests to the review pages, then parse the HTML content, and finally extract desired data elements.
To scrape more than 10 pages of Amazon reviews, you can implement pagination by modifying the page number in the URL and iterating through the pages programmatically.
ScrapeHero provides a comprehensive pricing plan for both Scrapers and APIs. To know more about the pricing, visit our pricing page.
The legality of web scraping depends on the legal jurisdiction, i.e., laws specific to the country and the locality. Gathering or scraping publicly available information is not illegal.








