This article outlines a few methods for Google Maps scraping. This could effectively export Google Maps data to Excel or other formats for easier access and use.
There are two methods for Google Maps scraping:
- Scrape Google Maps with coding: Building a web scraper in Python or JavaScript
- Scrape Google Maps without coding: Using the ScrapeHero Cloud’s Google Maps Search Results Scraper, a no-code scraping tool
ScrapeHero Cloud offers you ready-made web crawlers and real-time APIs, which are the easiest way to extract data from websites and download it into spreadsheets with a few clicks.
Don’t want to code? ScrapeHero Cloud is exactly what you need.
With ScrapeHero Cloud, you can download data in just two clicks!
If you don’t like or want to code, ScrapeHero Cloud is just right for you!
Skip the hassle of installing software, programming and maintaining the code. Download this data using ScrapeHero cloud within seconds.
Building a Web Scraper in Python or JavaScript to Extract Google Maps Data
In this section, we will guide you on how to scrape data from Google Maps using Python or JavaScript. We will utilize the browser automation framework Playwright, to emulate browser behavior in our code.
This method has advantages, including bypassing common blocks that have been put in place to prevent Google Maps scraping. However, familiarity with the Playwright API is necessary to use it effectively.
You could also use Python Requests, LXML, or BeautifulSoup to build a Google Map scraper without using a browser or a browser automation library. However, bypassing the anti-scraping mechanisms implemented can be challenging and is beyond the scope of this article.
Here are the steps for scraping Google Maps data using Playwright:
Step 1: Choose either Python or JavaScript as your programming language.
Step 2: Install Playwright for your preferred language:
Python
pip install playwright
# to download the necessary browsers
playwright installJavaScript
npm install playwright@latestStep 3: Write your code to emulate browser behavior and extract the desired data from Google Maps using the Playwright API. You can use the code:
Python
import asyncio
import json
from playwright.async_APIimport Playwright, async_playwright
from playwright.async_APIimport TimeoutError as PlaywrightTimeoutError
async def extract_details(page):
"""
Extracts the results information from the page
Args:
page: Playwright page object
Returns:
A list containing details of results as a dictionary. The dictionary has
title, review count, rating, address of various results
"""
# defining selectors
result_container_selector = 'div[role="article"]'
title_selector = '.fontHeadlineSmall span'
review_text_selector = '.ZkP5Je span'
address_selector = 'div.W4Efsd div.W4Efsd:nth-of-type(1) span[jsinstance'
'="*1"] span:not([aria-hidden="true"]):not([style'
'*="none"])'
phone_selector = 'div.W4Efsd div.W4Efsd:nth-of-type(2) span[jsins'
'tance="*1"] span:not([aria-hidden="true"]):not([sty'
'le*="none"])'
results_parsed = []
results = page.locator(result_container_selector)
# iterating through all the displayed results
for result_idx in range(await results.count()):
# extracting individual results
result_elem = results.nth(result_idx)
# extracting the title
title = await result_elem.locator(title_selector).inner_text()
# extracting and cleaning review details
review_raw = await result_elem.locator(
review_text_selector).all_inner_texts()
rating = float(review_raw[0])
review_count = review_raw[1].replace('(', '').replace(')', '')
# extracting address
try:
address = await result_elem.locator(address_selector).inner_text()
except PlaywrightTimeoutError:
# address may not be available
address = None
# extracting phone
try:
phone = await result_elem.locator(phone_selector).inner_text()
except PlaywrightTimeoutError:
# phone may not be available
phone = None
data = {
'title': title,
'review_count': review_count,
'rating': rating,
'address': address,
'phone': phone
}
results_parsed.append(data)
return results_parsed
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
"""
Main function which launches browser instance and performs browser
interactions
Args:
playwright: Playwright instance
"""
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(
headless=False,
proxy={'server': 'proxy url here'}
)
context = await browser.new_context()
# overriding timeout
context.set_default_timeout(100000)
search_term = "dentist in New York City, NY, USA"
# Open new page
page = await context.new_page()
# Go to https://www.google.com/maps/
await page.goto("https://www.google.com/maps/")
# Click [aria-label="Search Google Maps"]
await page.locator("[aria-label="Search Google Maps"]").click()
# Fill input[name="q"]
await page.locator("input[name="q"]").fill(search_term)
# click search button
await page.locator("button[id="searchbox-searchbutton"]").click()
# waiting for results to be displayed on the page
await page.wait_for_selector('div[role="article"]')
results = await extract_details(page)
# saving the data
with open('restaurant_data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(results, f, indent=2)
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
async def main() -> None:
async with async_playwright() as playwright:
await run(playwright)
asyncio.run(main())JavaScript
// importing required modules
import fs from 'fs';
// initializing the required browser
import playwright from 'playwright';
/**
* Open browser, goto given url and collect data
*/
async function run() {
const browser = await playwright.chromium.launch({
headless: false
});
const context = await browser.newContext({
proxy: { server: 'http://ProxyIP:Port' }
});
// Open new page
const page = await context.newPage();
// Go to https://www.google.com/maps
await page.goto('https://www.google.com/maps', { waitUntil: 'load' });
// Click on search tab
await page.locator('[aria-label="Search Google Maps"]').click();
// Enter the search query
await page.locator('[aria-label="Search Google Maps"]').type('restaurants near New York, NY, USA', { 'delay': 500 });
// Press Enter after entering the query
await page.locator('[aria-label="Search Google Maps"]').press('Enter');
let ListingPageData = await extractDetails(page);
// Save data as JSON
const jsonData = JSON.stringify(ListingPageData);
saveJSONFile(jsonData);
// Closing browser context after use
await context.close();
await browser.close();
};
/**
* Extract data from HTML content
* @param page - Page object
* @returns {JSON} - Return collected data in JSON format
*/
async function extractDetails(page) {
// Wait for results
let listedProductSelector = 'div[role="article"]';
await page.waitForSelector(listedProductSelector);
let results = page.locator(listedProductSelector);
// Now we need to collect details from HTML content.
let ListingPageData = [];
let resultCount = await results.count();
// All the selectors used to collect data
let reviewTextSelector = '.ZkP5Je span';
let addressSelector = 'div.W4Efsd div.W4Efsd:nth-of-type(1) span[jsinstance="*1"] span:not([aria-hidden="true"]):not([style*="none"])';
let phoneSelector = 'div.W4Efsd div.W4Efsd:nth-of-type(2) span[jsinstance="*1"] span:not([aria-hidden="true"]):not([style*="none"])';
let titleSelector = `.fontHeadlineSmall span`;
// Iterate through each search result and save data to a list variable
for (let i = 0; i < resultCount; i++) {
let resultElem = results.nth(i);
let title = await resultElem.locator(titleSelector).innerText();
let reviewRaw = await resultElem.locator(reviewTextSelector).allInnerTexts();
let rating = reviewRaw[0];
let reviewCount = reviewRaw[1].replace('(', '').replace(')', '');
let address = null;
let phone = null;
try {
address = await resultElem.locator(addressSelector).innerText();
}
catch (err) {
console.log("Address was not found!");
};
try {
phone = await resultElem.locator(phoneSelector).innerText();
}
catch (err) {
console.log("Phone number was not found!");
};
let productData = {
title: title,
reviewCount: reviewCount,
rating: rating,
address: address,
phone: phone
};
console.log(productData);
ListingPageData.push(productData);
};
return ListingPageData;
};
/**
* Save JSON data to .json file
* @param jsonData - Extracted data in JSON format
*/
async function saveJSONFile(jsonData) {
fs.writeFile("data.json", jsonData, 'utf8', function (err) {
if (err) {
console.log("An error occurred while writing JSON Object to File.");
return console.log(err);
};
console.log("JSON file has been saved.");
});
};
run();This code shows scraping Google Maps’ restaurant information using Playwright in both Python and JavaScript.
The corresponding scripts have two main functions, namely:
- run function: This function takes a Playwright instance as an input and performs the scraping process. It launches a Chromium browser instance, navigates to Google Maps, fills in a search term, clicks the search button, and waits for the results to be displayed on the page.
The extract_details function is then called to extract the restaurant details and store the data in a JSON file.
- extract_details function: This function takes a Playwright page object as an input and returns a list of dictionaries containing restaurant details. The details include the title, review count, rating, address, and phone number of each restaurant.
Finally, the main function uses the async_playwright context manager to execute the run function. A JSON file containing the listings of the Google Maps script that you just executed will be created.
Step 4: Run your code and collect the scraped data from Google Maps.
You can access the code for Google Maps in Python and JavaScript on GitHub.
Using No-Code Google Maps Scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud
The Google Maps scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud is a convenient solution for scraping Google Maps search results. It provides an easy, no-code method for scraping Google Maps, making it accessible for individuals with limited technical skills.
In this section, we’ll guide you through the steps required to set up and use the Google Map scraper.
1. Sign up or log in to your ScrapeHero Cloud account.
2. Go to the ScrapeHero Google Maps Search Results Scraper by ScrapeHero Cloud.
3. Click the Create New Project button.
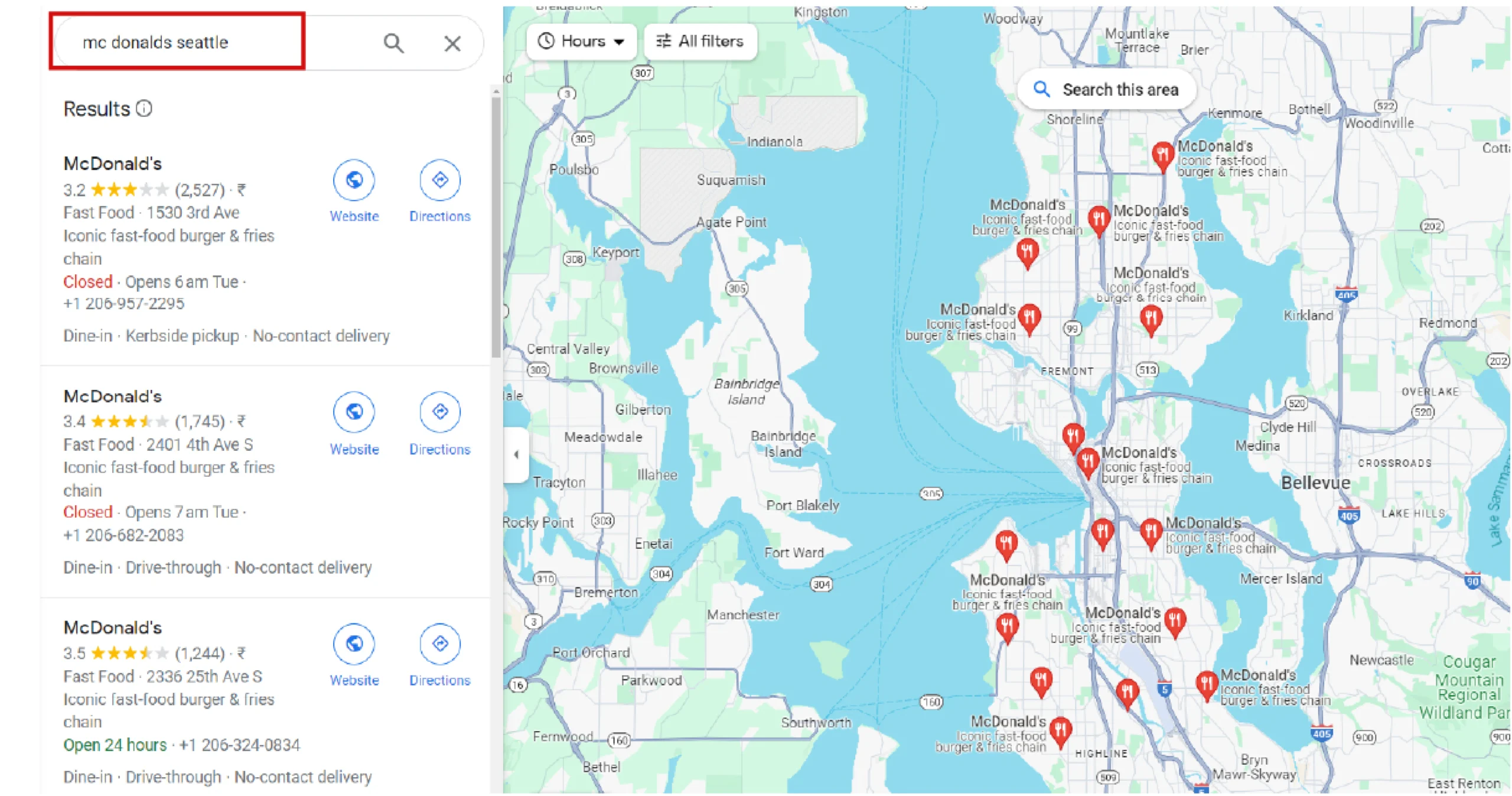
4. ScrapeHero Google Maps scraper allows you to search with a query. A query is a question or a phrase about what your requirement is, say, McDonalds in Seattle. This you can verify in Google Maps, as shown.
5. In the field provided, enter a project name, search query, and the maximum number of records you want to gather. Then, click the Gather Data button to start the scraper.
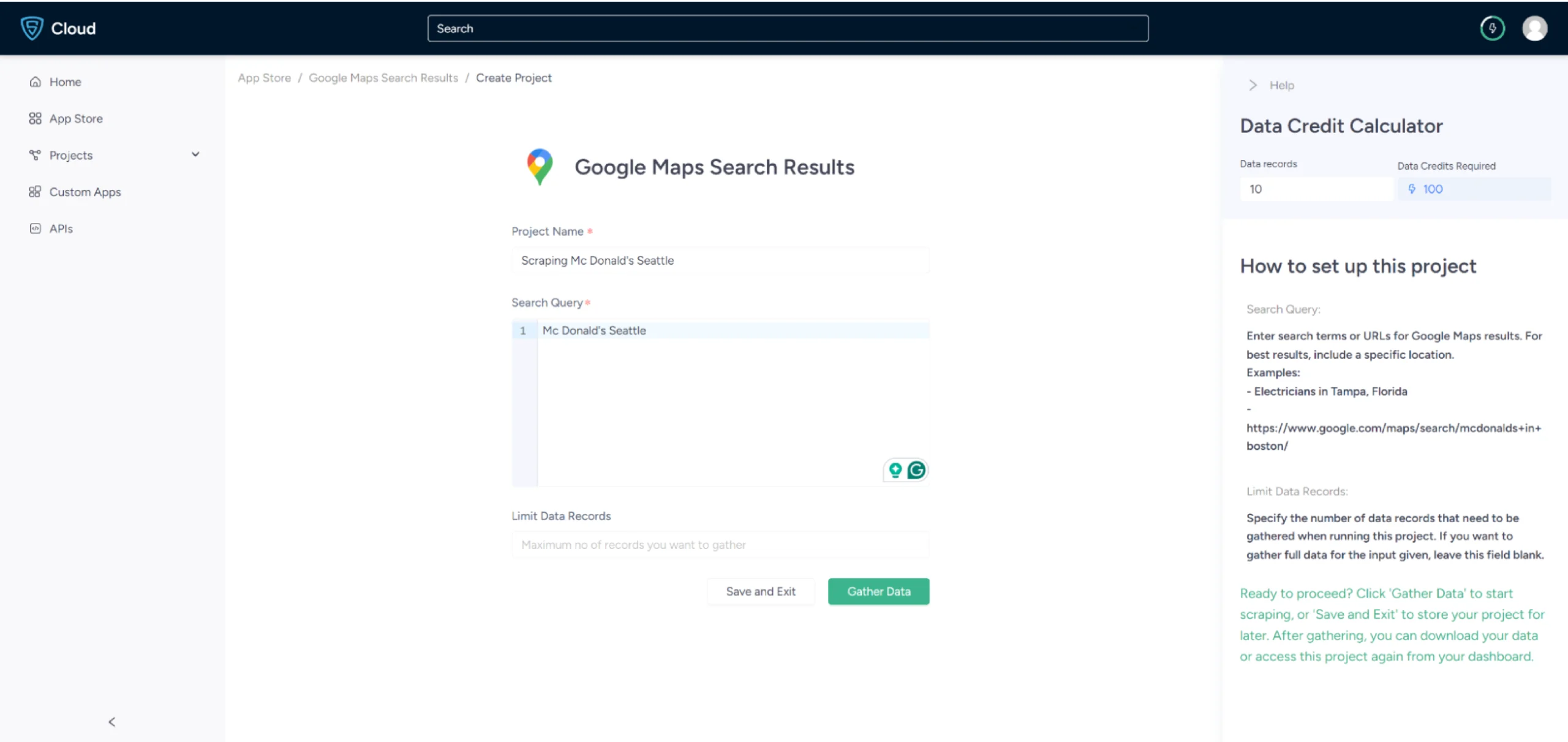
6.The scraper will start fetching data for your queries, and you can track its progress under the Projects tab.
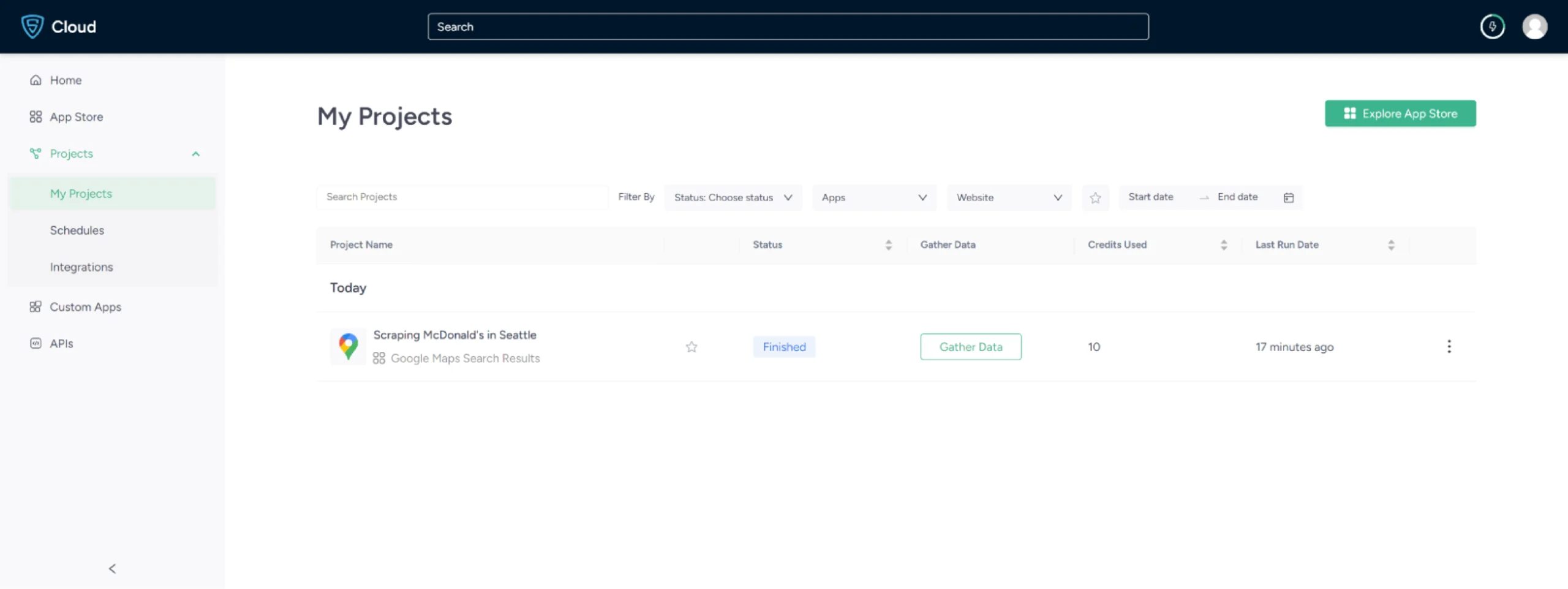
7. Once it is finished, you can view the data by clicking on the project name. A new page will appear, and under the Overview tab, you can see and download the data.
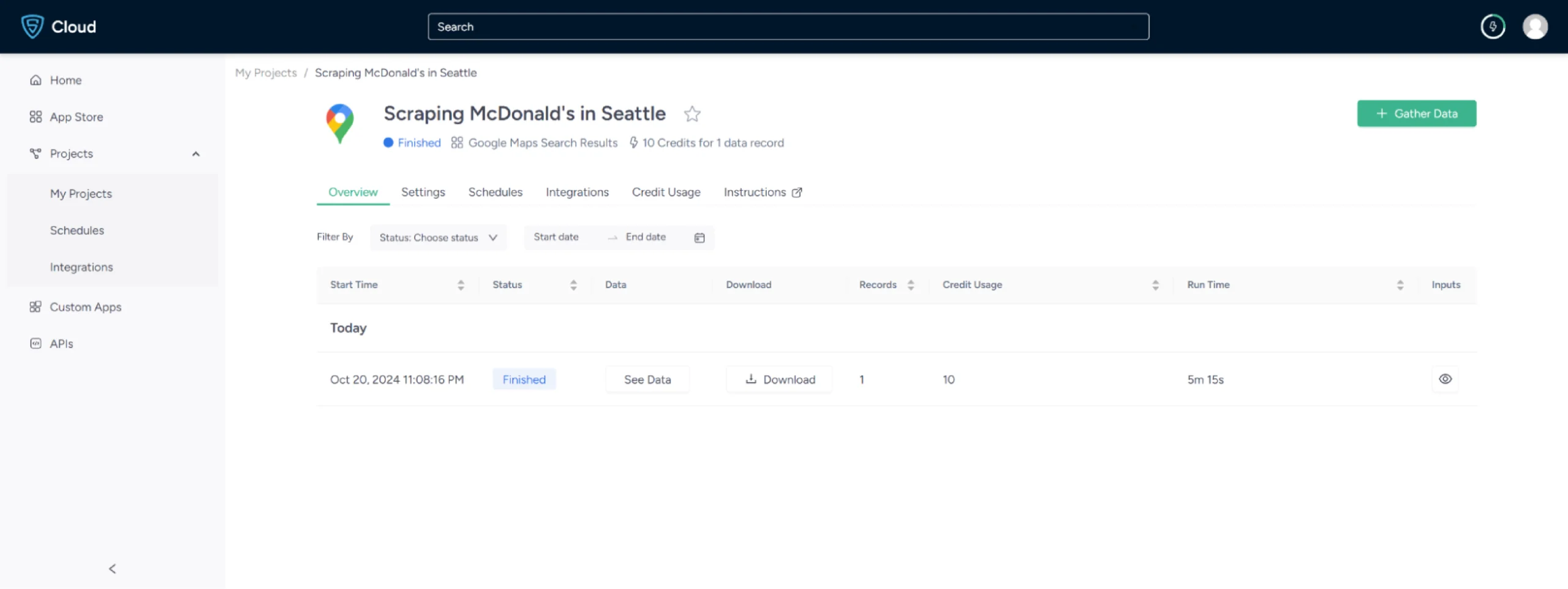 8. You can also pull Google Maps data into a spreadsheet from here. Just click on Download Data, select Excel, and open the downloaded file using Microsoft Excel.
8. You can also pull Google Maps data into a spreadsheet from here. Just click on Download Data, select Excel, and open the downloaded file using Microsoft Excel.
Use Cases of Google Maps Data
If you’re unsure as to why you should scrape, then here are some use cases for the location data from Google Maps:
-
Location-Based Marketing
By scraping Google Maps, you will get location data that can be used to target advertising and promotional messages to users based in those locations.
-
Lead Generation
Analyzing business locations, contact information, and other data points can help in generating leads, mainly for B2B opportunities based on location.
-
Brand Sentiment
Customer reviews and ratings data from Google Maps on business listings can help determine the general sentiment toward a particular business.
-
Competitor Analysis
Google Maps data can be used to map out competitor locations, analyze competitor reviews and activities, such as hours of operation and new products, and identify gaps in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Scraping Google Maps means extracting data from Google Maps listings, including business names, addresses, phone numbers, reviews, and popular times.
Google Maps API is costly and challenging to set up, making it a significant cost for large-scale projects, while ScrapeHero Cloud offers a cheaper alternative.
ScrapeHero provides a comprehensive pricing plan for both Scrapers and APIs. To know more about the pricing, visit our pricing page.
Choosing the best Google Maps data scraper is challenging due to legal, ethical, and technical considerations.
However, you can use the ScrapeHero Google Maps Scraper or the ScrapeHero Google Reviews Scraper from ScrapeHero Cloud to extract details related to Google Maps as a safer option.
The legality of web scraping depends on the jurisdiction, but it is generally considered legal if you are scraping publicly available data.
You can use web scraping tools like ScrapeHero to extract data on points of interest from Google Maps.
You can scrape tables from Google Maps by selecting and extracting structured data using a scraper that can interpret HTML tables.
The advantages of scraping Google Maps data for businesses include market research, lead generation, and optimizing operations.








