Is web crawling legal? Crawling a website isn’t illegal. The legality of web crawling depends on a number of factors, including purpose, respecting website rules, data privacy, etc.
This blog will serve as your guide to understanding the legality of web crawling and will answer the many questions surrounding it.
Legal Considerations for Crawling Websites Legally
The question whether it is legal to crawl websites or not cannot be answered without considering the following aspects of the legality of web crawling.

Intellectual Property Rights and Web Crawling
The valuable assets of a company go beyond physical properties like buildings, machinery, etc, and also include its intellectual properties. Intellectual property rights are the legal frameworks in place to protect the intellectual properties of people and organizations.
Web crawling involves extracting data from websites that have all kinds of data, including copyrighted material, trademarks, patented information, etc. It is thus crucial to respect intellectual property rights, including copyright, trademark, and patent laws.
Care must be taken to ensure that the data extracted through web crawling does not infringe intellectual property rights. Articles and written content, images and photographs, videos and music, software code, and scripts, etc., are examples of data that are protected by intellectual property rights.
Terms of Service Violation and Web Crawling
Websites often have Terms of Service (ToS) agreements that outline the rules and restrictions while using their site. These agreements sometimes explicitly prohibit web crawling their content without permission. Violating these terms may invite legal consequences, including the website owner accusing you of breaching the contract.
However, for the Terms of Service to be enforceable, users must explicitly agree to the terms, often through a checkbox or clickwrap agreement during the login or signup process. Courts are more likely to uphold the ToS agreement if users have been explicitly asked to take an acceptance action.
Don’t want to code? ScrapeHero Cloud is exactly what you need.
With ScrapeHero Cloud, you can download data in just two clicks!
Data Privacy Laws and Web Crawling
People have the right to protect their personal information, and that is why data privacy laws exist. So, when web crawling involves extracting personal information from websites, it must comply with data privacy laws to ensure that individuals’ privacy is protected.
There is no universal data protection law that protects the privacy of individuals worldwide. However, many countries have their own data protection laws with provisions to protect their individuals’ privacy, like GDPR, CCPA, etc.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation in the European Union that sets the rules for how personal data is collected and processed. It applies to any organization that does business in the EU, regardless of where the business is located.
It dictates explicit consent from individuals before their personal data can be collected. It also mandates that data collection should be limited to what is necessary for the purpose. Individuals also have the right to access their data and request for its deletion. Organizations must be transparent about how they collect, use, and store personal data.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a law that was enacted to ensure the privacy rights and consumer protection of the residents of California. The law requires businesses to inform individuals about the data being collected and its purpose. It allows people the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information. They can also request access to their data and ask for it to be deleted.
Computer Fraud and Abuse Act and Web Crawling
The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) is a US law enacted in 1986 to fight hacking and unauthorized access to computer systems. It is an important law to consider if your intent is to crawl websites legally because it defines the legal boundaries and potential liabilities of accessing computer systems without authorization.
CFAA was invoked during the trials of the famous LinkedIn vs. HiQ Labs Inc. However, the Ninth Circuit ruled that scraping publicly available data did not violate CFAA, emphasizing the importance of public access.
Trespass to Chattels and Web Crawling
Trespass to Chattels is the intentional interference with the personal possessions or chattels of another person. In the context of web crawling, trespass to chattels may include unauthorized web crawling activities that interfere with a website’s servers or data. Courts have confirmed the occurrence of trespass to chattels in cases where web crawling has interfered with a computer system, leading to issues like website crashes or server overload.
Thus web crawling for data extraction can potentially raise concerns related to trespass to chattels if the crawling activity results in harm to the website or its servers.
Ethical Considerations While Crawling Websites
Ethical considerations when web crawling are the principles and guidelines that govern morally acceptable behavior while extracting data from websites. Following are some of the things you can consider when web crawling:

Respect Website Owners’ Wishes
If a website has a robots.txt file or any other clear instructions that prohibit crawling, it is considered unethical to crawl the site. In case you want to crawl such a site that has anti-crawling measures in place, it is advisable to contact the site owner for permission.
Avoid Overloading Servers
Crawling websites too quickly, with very little time between requests, can overload servers, making them unavailable for legitimate users. To avoid negatively impacting the website, you can be polite in doing your business by delaying requests, respecting robots.txt, and limiting requests per second.
Protect User Privacy
In the case of accessing personal information about website users, avoid storing or sharing any personally identifiable information (PII) you come across. Make sure to consolidate data into broader, more generalized categories to safeguard the privacy of individuals.
Respect Copyright
Copying large portions of copyrighted content without permission can constitute copyright infringement. Avoid scraping copyrighted text, images, or other content. In case you want such data, link to original sources instead of duplicating content.
Transparency and Consent
Be transparent about your identity and intentions as a crawler by providing a clear user agent string when crawling a website. Also, respond promptly to any outreach from website owners. Obtain consent if you plan to use the scraped data for commercial purposes.
Minimize Harm
Always weigh the potential benefits of your crawling project against any possible negative impacts on websites, users, or the internet ecosystem as a whole. Crawl only what you need and delete data you don’t use. The best way to go about it is to aim to create new value from the data rather than duplicating it.
Common Misconceptions Around the Legality of Crawling Websites
Before we close our discussion about the legality of crawling websites, let us bust a few misconceptions that people have about web crawling.
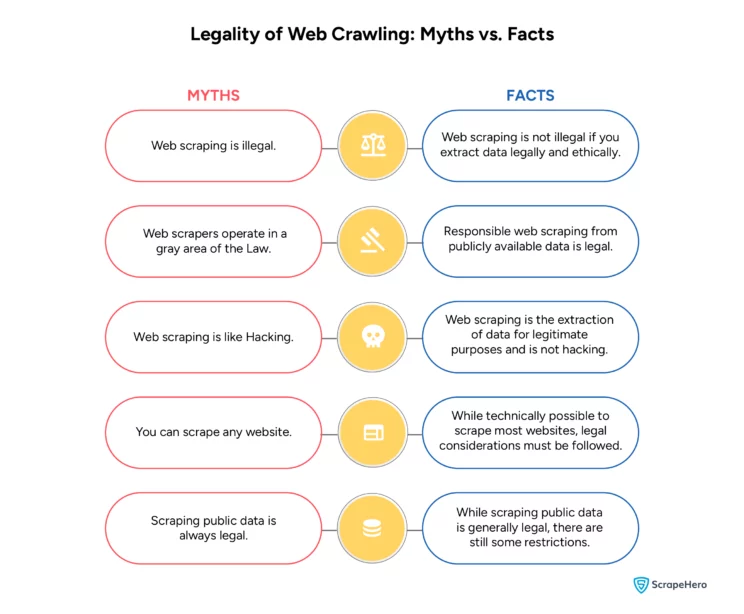
Is web crawling legal is thus not a simple yes or no question. The legality of web crawling depends on a number of factors, like the area of jurisdiction, purpose of use, terms of service, copyright issues, privacy considerations, nature of data, etc.
However, navigating through these factors might be tedious for those whose strong suit does not include web crawling. In this case, outsourcing your data requirements to a web crawling service provider like ScrapeHero would be a wise choice. With over a decade of experience in the field, we know everything that is there to know about crawling websites legally.