NASDAQ is a great source for stock market data. We will demonstrate how to write a scraper that will extract some key stock data based on a company’s ticker symbol.
In this tutorial, we will extract the summary quote for a public company from Nasdaq.
What data are we extracting?
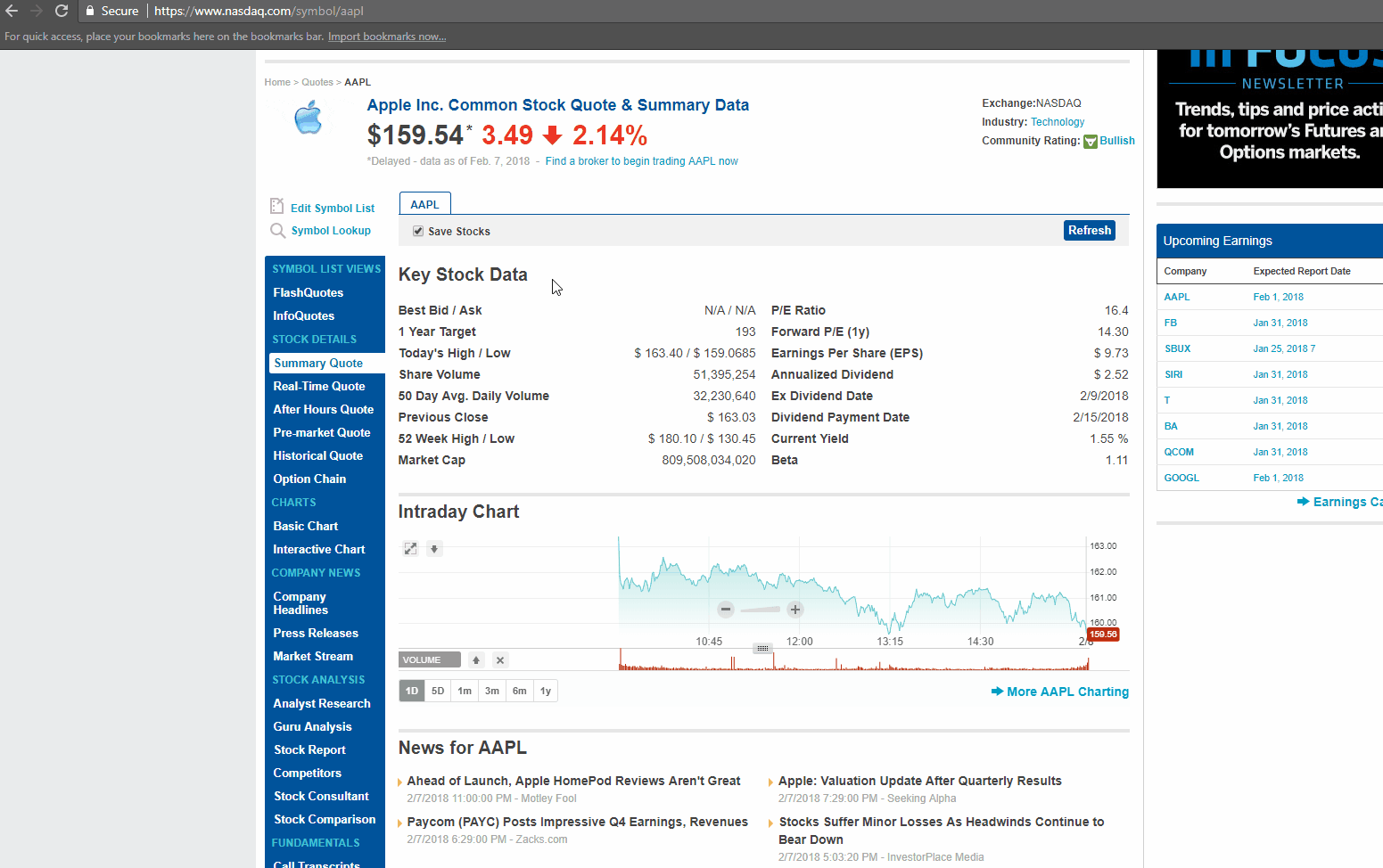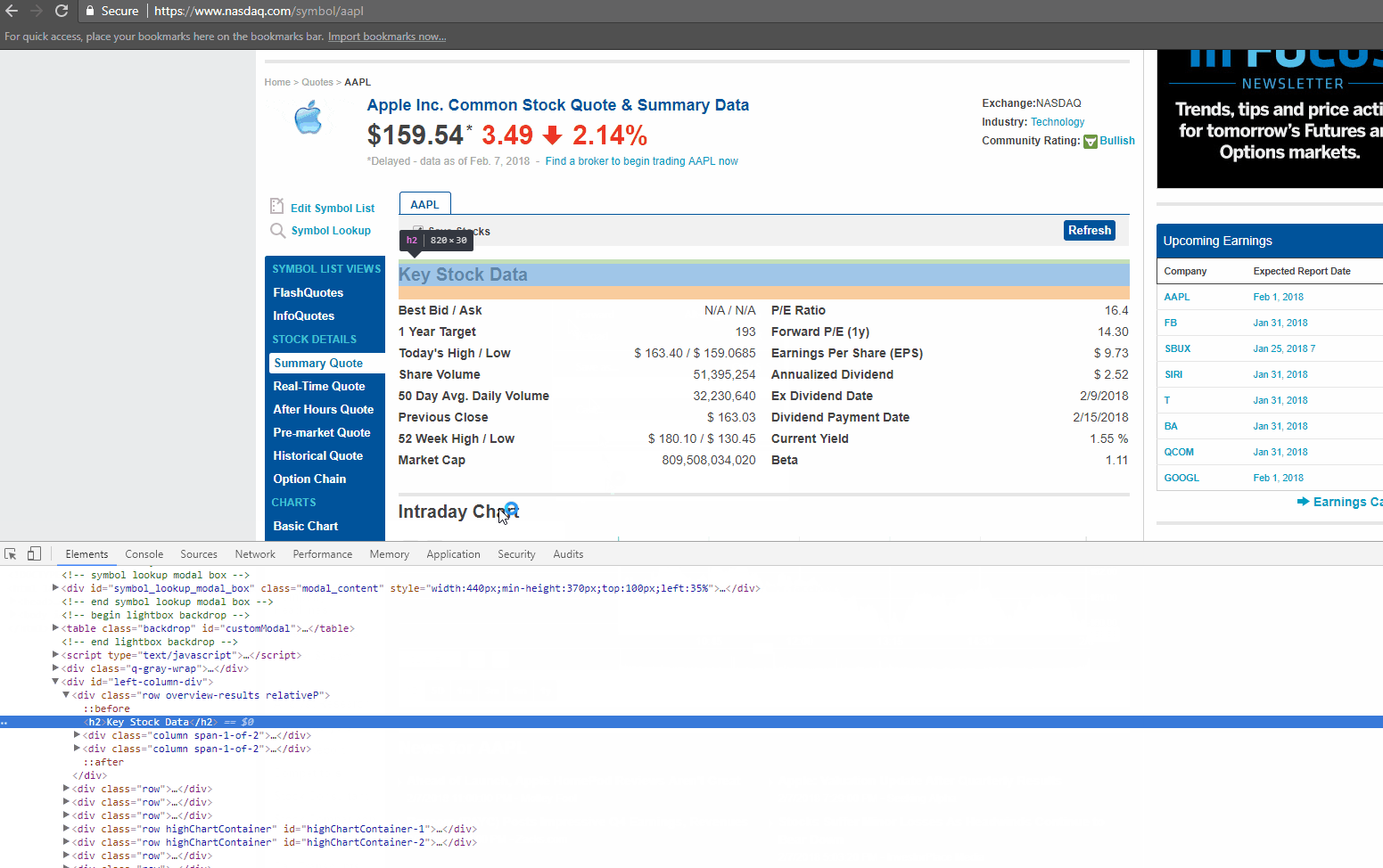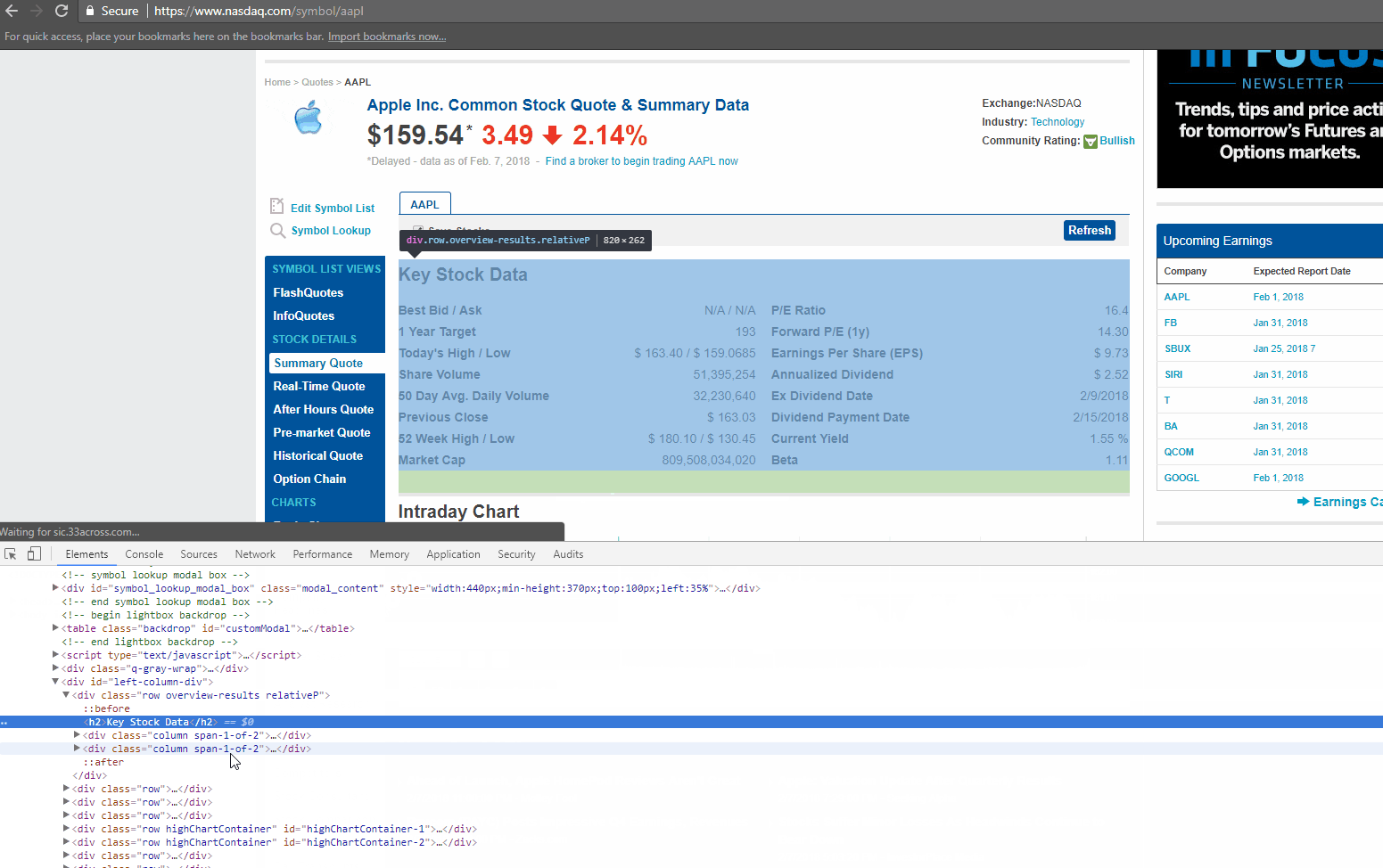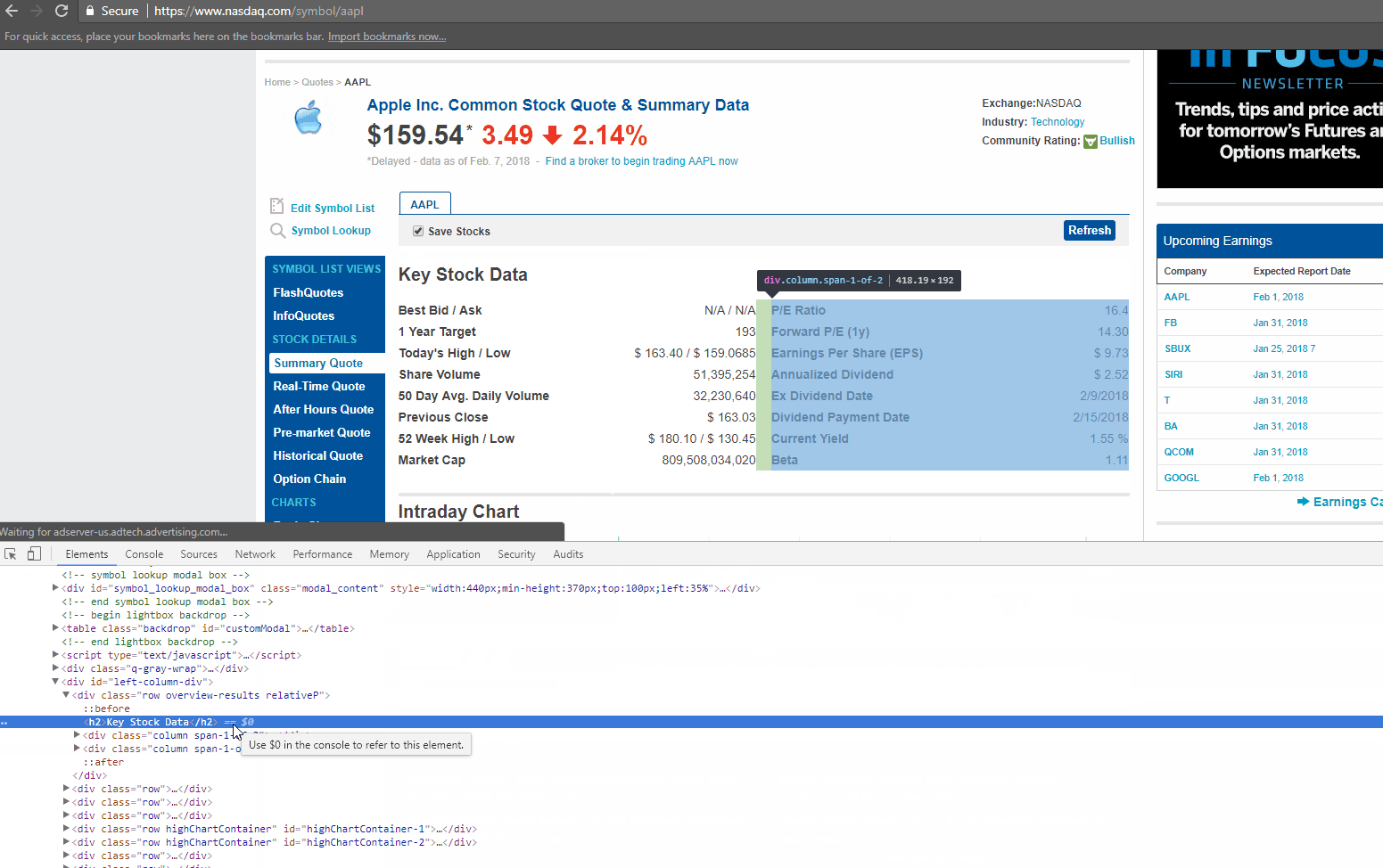
Here is the list of fields we will be extracting:
- Best Bid/Ask
- 1 Year Target
- Share Volume
- 50 Day Avg. Daily Volume
- Previous Close
- 52 Week High/Low
- Market Cap
- P/E Ratio
- Forward P/E (1y)
- Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- Annualized Dividend
- Ex-Dividend Date
- Dividend Payment Date
- Current Yield
- Beta
- Open Price
- Open Date
- Close Price
- Close Date
Read More – Learn to scrape Ebay product data
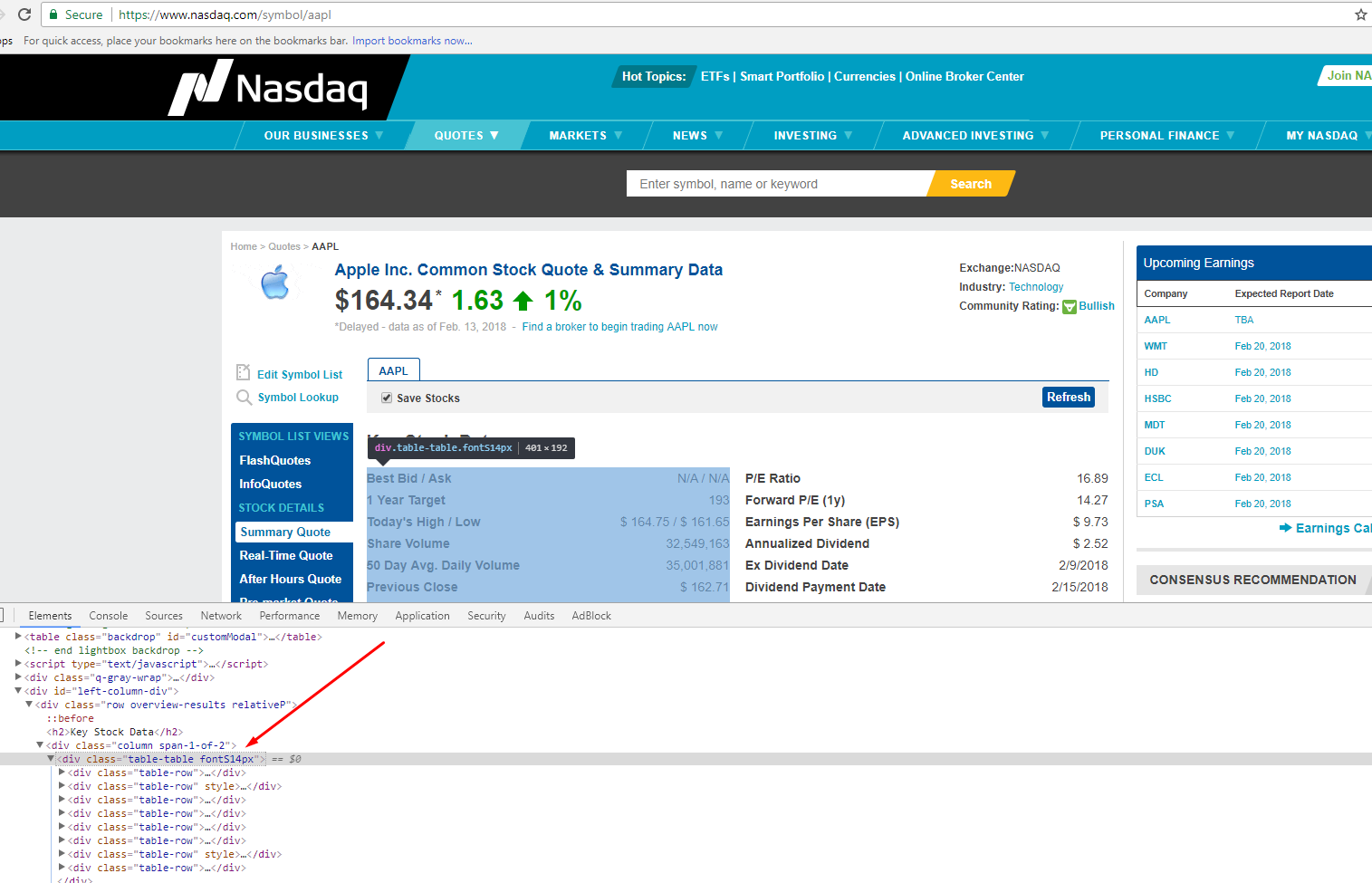
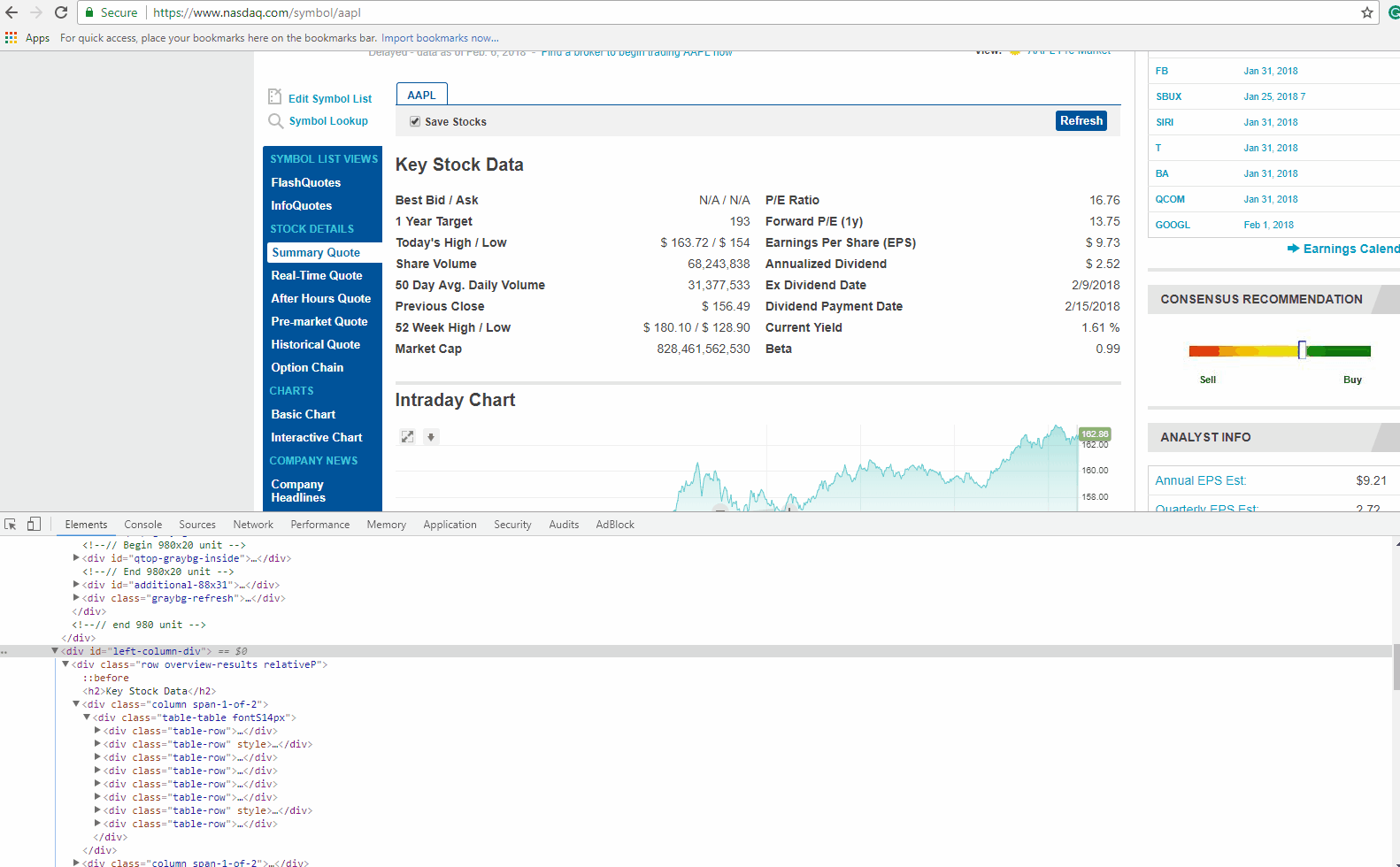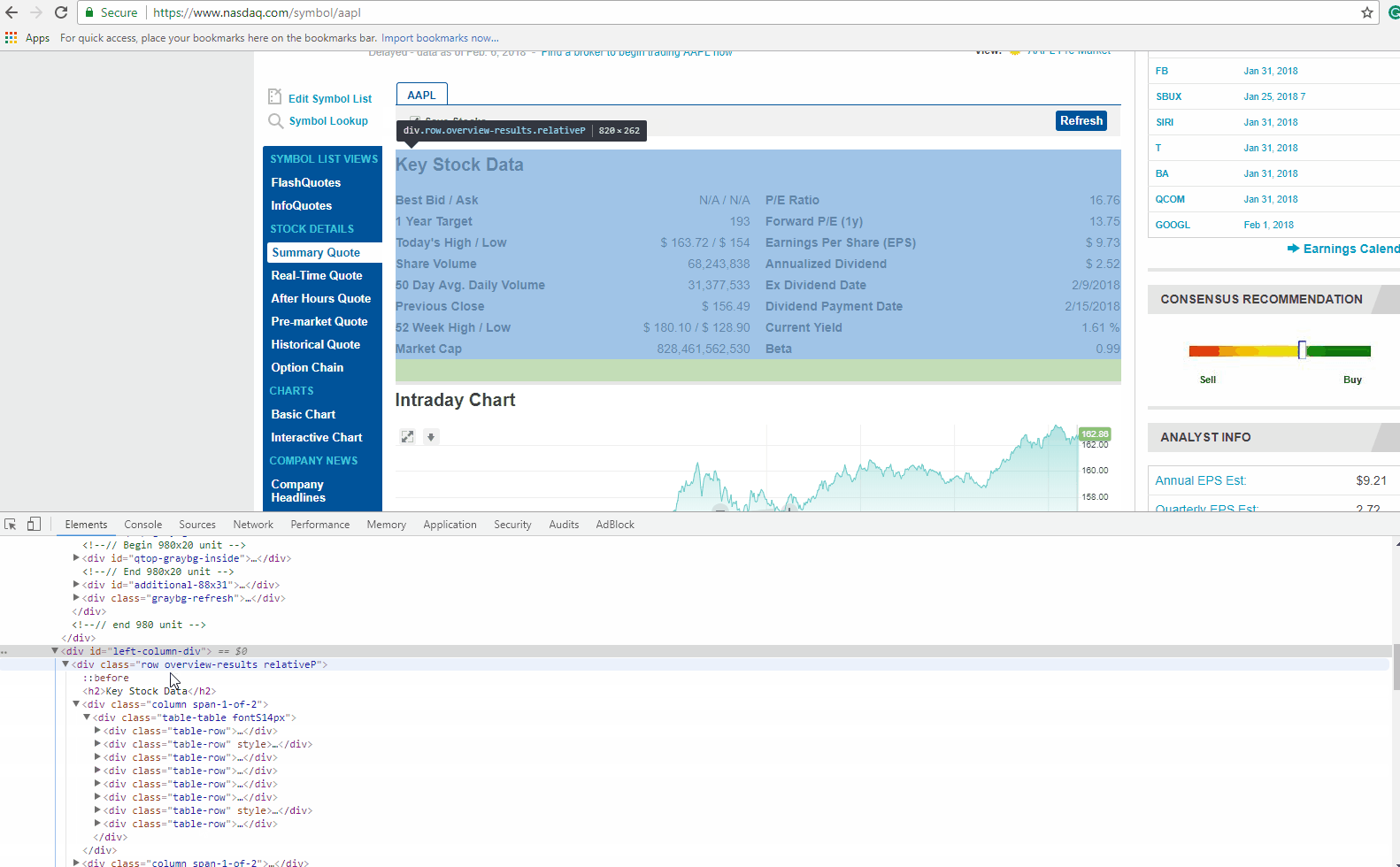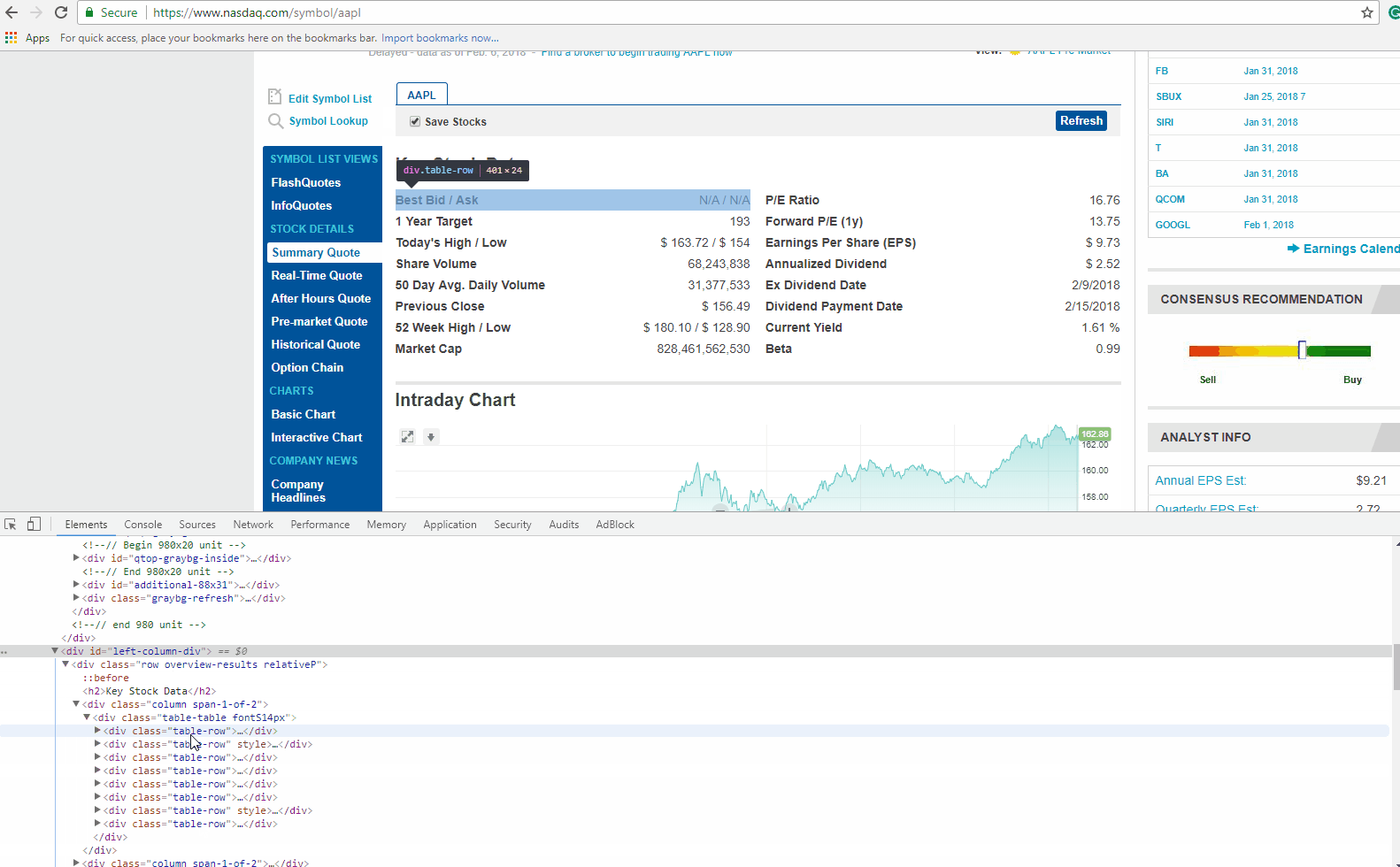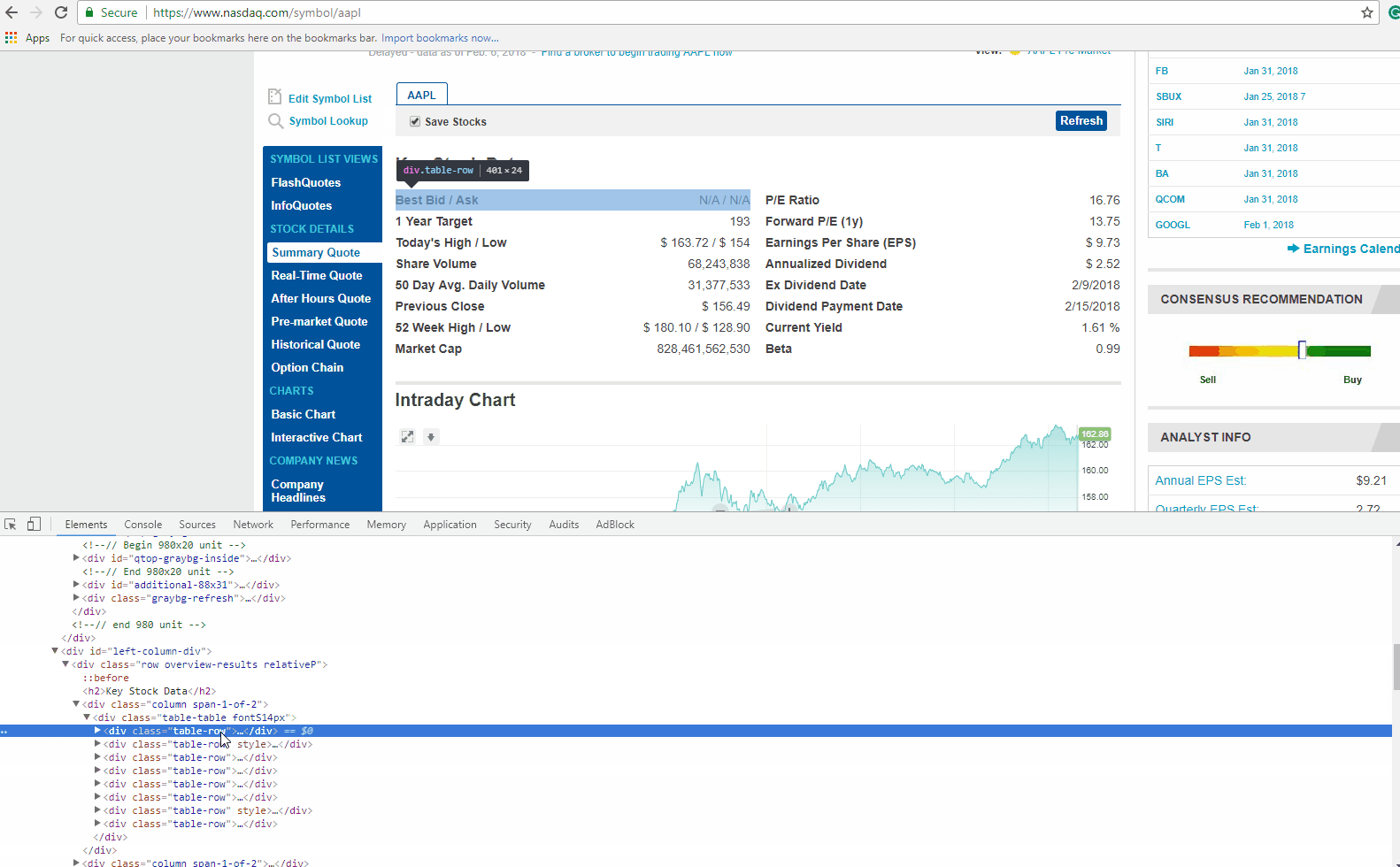
Below is a screenshot of the data we will be extracting.
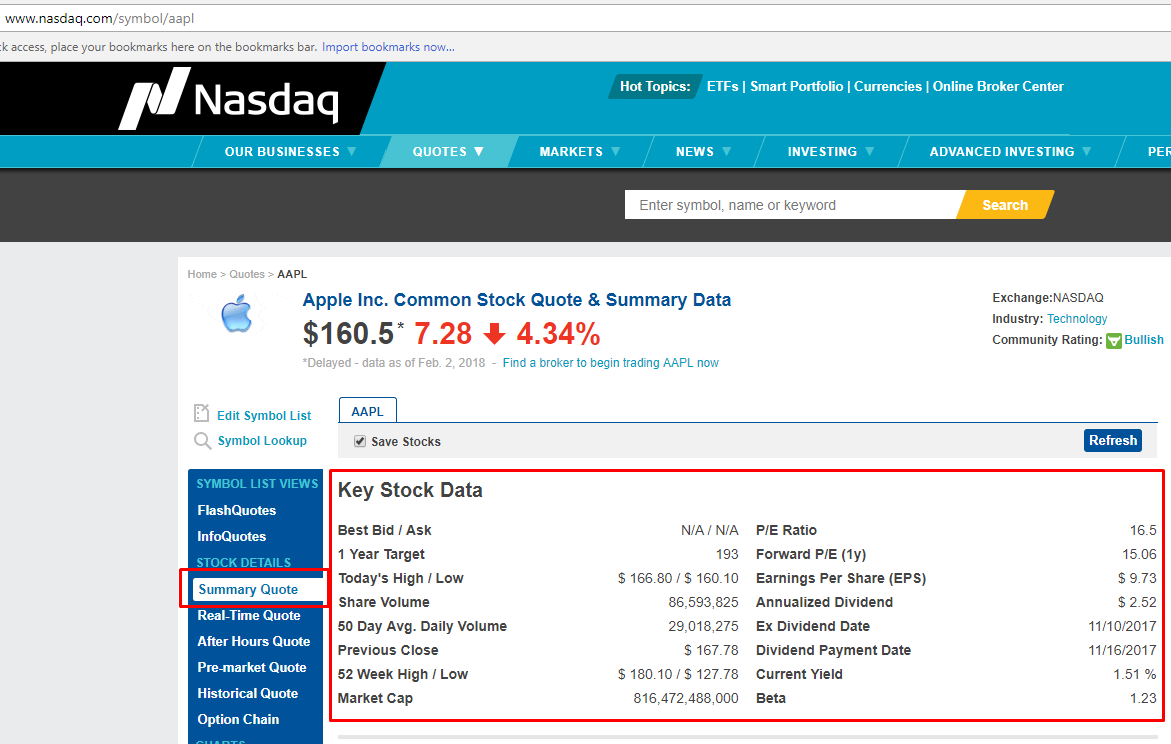
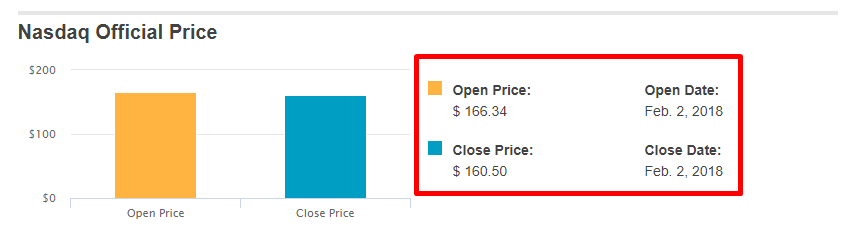
Finding the Data
Before we start building the scraper, we need to find where the data is present in the web page’s HTML Tags. You need to understand the HTML tags inside the page’s content to do so.
We assume you already understand HTML and know to code in Python. You don’t need advanced programming skills for the most part of this tutorial,
If you don’t know much about HTML and Python, spend some time reading Getting started with HTML – Mozilla Developer Network and https://www.programiz.com/python-programming
Let’s inspect the HTML of the web page and find out where the data is. Here is our logic
- Find the tag that encloses the list of links
- Get links from it and extract data
Inspecting the HTML
Open a browser (we are using Chrome here) and go to http://www.nasdaq.com/symbol/aapl
Right-click on any link on the page and choose – Inspect Element. The browser will open a toolbar and show the HTML Content of the Web Page, formatted nicely.
If you look closely at the GIF above, there is DIV tag, with its attribute called ‘class’ as ‘table-table’. This DIV encloses the data we need to extract.
Now let’s find the HTML tag(s) which has the links we need to extract. You can right-click on the link title in the browser and do inspect element again. It will open the HTML Content like before, and highlight the tag which holds the data you right clicked on
How to set up your computer for web scraper development
We will use Python 3 for this tutorial. The code will not run if you are using Python 2.7. To start, you need a computer with Python 3 and PIP installed in it.
Most UNIX operating systems like Linux and Mac OS comes with Python pre-installed. But, not all the Linux Operating Systems ship with Python 3 by default.
Let’s check your python version. Open a terminal ( in Linux and Mac OS ) or Command Prompt ( on Windows ) and type
python --version
and press enter. If the output looks something like Python 3.x.x, you have Python 3 installed. If it says Python 2.x.x you have Python 2. If it prints an error, you don’t probably have python installed.
If you don’t have Python 3, install it first.
Install Python 3 and Pip
Here is a guide to install Python 3 in Linux – http://docs.python-guide.org/en/latest/starting/install3/linux/
Mac Users can follow this guide – http://docs.python-guide.org/en/latest/starting/install3/osx/
Windows Users go here – https://www.scrapehero.com/how-to-install-python3-in-windows-10/
Install Packages
- Python Requests, to make requests and download the HTML content of the pages ( http://docs.python-requests.org/en/master/user/install/).
- Python LXML, for parsing the HTML Tree Structure using Xpaths (Learn how to install that here – http://lxml.de/installation.html)
Don’t want to code? ScrapeHero Cloud is exactly what you need.
With ScrapeHero Cloud, you can download data in just two clicks!
Read More – Learn to scrape Yelp business data
The Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from lxml import html
import requests
from time import sleep
import json
import argparse
from random import randint
def parse_finance_page(ticker):
"""
Grab financial data from NASDAQ page
Args:
ticker (str): Stock symbol
Returns:
dict: Scraped data
"""
key_stock_dict = {}
headers = {
"Accept":"text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Encoding":"gzip, deflate",
"Accept-Language":"en-GB,en;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,ml;q=0.7",
"Connection":"keep-alive",
"Host":"www.nasdaq.com",
"Referer":"http://www.nasdaq.com",
"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests":"1",
"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.119 Safari/537.36"
}
# Retrying for failed request
for retries in range(5):
try:
url = "http://www.nasdaq.com/symbol/%s"%(ticker)
response = requests.get(url, headers = headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code!=200:
raise ValueError("Invalid Response Received From Webserver")
print("Parsing %s"%(url))
# Adding random delay
sleep(randint(1,3))
parser = html.fromstring(response.text)
xpath_head = "//div[@id='qwidget_pageheader']//h1//text()"
xpath_key_stock_table = '//div[@class="row overview-results relativeP"]//div[contains(@class,"table-table")]/div'
xpath_open_price = '//b[contains(text(),"Open Price:")]/following-sibling::span/text()'
xpath_open_date = '//b[contains(text(),"Open Date:")]/following-sibling::span/text()'
xpath_close_price = '//b[contains(text(),"Close Price:")]/following-sibling::span/text()'
xpath_close_date = '//b[contains(text(),"Close Date:")]/following-sibling::span/text()'
xpath_key = './/div[@class="table-cell"]/b/text()'
xpath_value = './/div[@class="table-cell"]/text()'
raw_name = parser.xpath(xpath_head)
key_stock_table = parser.xpath(xpath_key_stock_table)
raw_open_price = parser.xpath(xpath_open_price)
raw_open_date = parser.xpath(xpath_open_date)
raw_close_price = parser.xpath(xpath_close_price)
raw_close_date = parser.xpath(xpath_close_date)
company_name = raw_name[0].replace("Common Stock Quote & Summary Data","").strip() if raw_name else ''
open_price =raw_open_price[0].strip() if raw_open_price else None
open_date = raw_open_date[0].strip() if raw_open_date else None
close_price = raw_close_price[0].strip() if raw_close_price else None
close_date = raw_close_date[0].strip() if raw_close_date else None
# Grabbing ans cleaning keystock data
for i in key_stock_table:
key = i.xpath(xpath_key)
value = i.xpath(xpath_value)
key = ''.join(key).strip()
value = ' '.join(''.join(value).split())
key_stock_dict[key] = value
nasdaq_data = {
"company_name":company_name,
"ticker":ticker,
"url":url,
"open price":open_price,
"open_date":open_date,
"close_price":close_price,
"close_date":close_date,
"key_stock_data":key_stock_dict
}
return nasdaq_data
except Exception as e:
print("Failed to process the request, Exception:%s"%(e))
if __name__=="__main__":
argparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
argparser.add_argument('ticker',help = 'Company stock symbol')
args = argparser.parse_args()
ticker = args.ticker
print("Fetching data for %s"%(ticker))
scraped_data = parse_finance_page(ticker)
print("Writing scraped data to output file")
with open('%s-summary.json'%(ticker),'w') as fp:
json.dump(scraped_data,fp,indent = 4,ensure_ascii=False)
Execute the full code with the script name followed by the ticker symbol of the company’s stock data you would like:
python3 nasdaq_finance.py stock symbol
As an example, let’s find the summary data for Apple Inc. The script would be executed as:
python3 nasdaq_finance.py aapl
You should see a file AAPL-summary.json called in the same folder as the script, with the extracted data. Here is some sample data extracted from Nasdaq.com for the command above.
{
"company_name": "Apple Inc.",
"ticker": "AAPL",
"url": "http://www.nasdaq.com/symbol/AAPL",
"open price": "$ 167.24",
"open_date": "Feb. 1, 2018",
"close_price": "$ 167.43",
"close_date": "Jan. 31, 2018",
"key_stock_data": {
"Best Bid / Ask": "$ 167.95 / $ 167.96",
"1 Year Target": "193",
"Today's High / Low": "$ 168.26 / $ 166.76",
"Share Volume": "15,654,756",
"50 Day Avg. Daily Volume": "28,511,634",
"Previous Close": "$ 167.43",
"52 Week High / Low": "$ 180.10 / $ 127.01",
"Market Cap": "854,371,055,200",
"P/E Ratio": "18.26",
"Forward P/E (1y)": "15.04",
"Earnings Per Share (EPS)": "$ 9.20",
"Annualized Dividend": "$ 2.52",
"Ex Dividend Date": "11/10/2017",
"Dividend Payment Date": "11/16/2017",
"Current Yield": "1.51 %",
"Beta": "1.27"
}
}
The data will be saved as a JSON file. Instead of writing the data to a JSON file you can connect it to a MySQL database.
You can download the code at https://gist.github.com/scrapehero/c7794d9e4522d9c72ba167496b849228. Let us know in the comments how this scraper worked for you.
Known Limitations
This code should be capable of scraping the details of most ticker symbols. If you want to scrape the details of thousands of companies you should read Scalable do-it-yourself scraping – How to build and run scrapers on a large scale and How to prevent getting blacklisted while scraping .
If you need some professional help with scraping websites contact us by filling up the form below.
We can help with your data or automation needs
Turn the Internet into meaningful, structured and usable data
Disclaimer: Any code provided in our tutorials is for illustration and learning purposes only. We are not responsible for how it is used and assume no liability for any detrimental usage of the source code. The mere presence of this code on our site does not imply that we encourage scraping or scrape the websites referenced in the code and accompanying tutorial. The tutorials only help illustrate the technique of programming web scrapers for popular internet websites. We are not obligated to provide any support for the code, however, if you add your questions in the comments section, we may periodically address them.